
Moodle 3.x Developer's Guide
Ian Wild
- 368 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Moodle 3.x Developer's Guide
Ian Wild
À propos de ce livre
Effortlessly ensure your application's code quality from day 1About This Book• Customize your Moodle 3.x app.• Leverage the new features of Moodle 3.x by diving deep into the Moodle development eco-system.• Cater to heavy user traffic, customize learning requirements and create custom third party plugins.Who This Book Is ForThis book is for Moodle developers who are familiar with the basic Moodle functionality and have an understanding of the types of scenarios in which the Moodle platform can be usefully employed. You must have medium-level PHP programming knowledge. You should be familiar with HTML and XML protocols. You do not need to have prior knowledge of Moodle-specific terminologyWhat You Will Learn• Work with the different types of custom modules that can be written for Moodle 3.x• Understand how to author custom modules so they conform to the agreed Moodle 3.x development guidelines• Get familiar with the Moodle 3.x architecture—its internal and external APIs• Customize Moodle 3.x so it can integrate seamlessly with third-party applications of any kind• Build a new course format to specify the layout of a course• Implement third-party graphics libraries in your plugins• Build plugins that can be themed easily• Provide custom APIs that will provide the means to automate Moodle 3 in real timeIn DetailThe new and revamped Moodle is the top choice for developers to create cutting edge e-learning apps that cater to different user's segments and are visually appealing as well.This book explains how the Moodle 3.x platform provides a framework that allows developers to create a customized e-learning solution. It begins with an exploration of the different types of plugin..We then continue with an investigation of creating new courses. You will create a custom plugin that pulls in resources from a third-party repository. Then you'll learn how users can be assigned to courses and granted the necessary permissions.Furthermore, you will develop a custom user home. At the end of the book, we'll discuss the Web Services API to fully automate Moodle 3.x in real time.Style and approachThis book takes a step-by-step practical approach with every step explained in great detail using practical examples. You will create custom plugins from scratch with the examples shown and create new modules as well as extensions with the examples presented.
Foire aux questions
Informations
Creative Teaching - Developing Custom Resources and Activities
- Knowing if a user story requires a resource or an activity
- How to manage files (including ZIP compressed files) using the File API
- The scripts required for course plugin installation and an understanding of their structure
- Knowing how to include JavaScript in your plugins--including passing parameters to JavaScript AMD modules
- How to support course backup and restore
- Introducing resources and activities
Teaching interactions

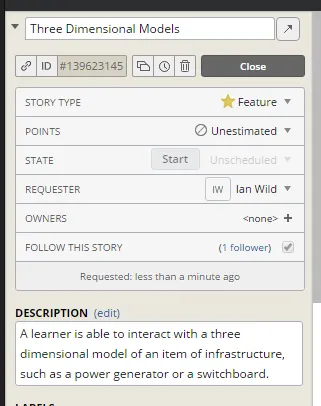
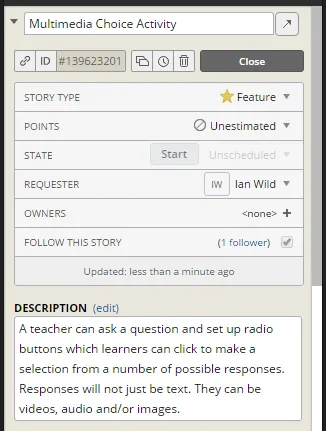
Interfaces. If you haven't yet read Chapter 3, Internal Interfaces then it might be worth doing so before continuing with this chapter. What's great about studying this particular plugin is that, in a broader context, it will give you a good understanding of how multimedia files can be handled in any plugin. Likewise, the development of the three-dimensional model viewer plugin--also explained in this chapter--will give you a thorough understanding of how to include third-party (specifically JavaScript) libraries in your plugins.