IN THIS PART …
Discover what blockchains are all about and how they can benefit your organization.
Identify the right type of technology and the steps to developing and executing an effective blockchain project.
Make your own smart contracts on Bitcoin, and determine where this technology can fit within your organization.
IN THIS CHAPTER
Discovering the new world of blockchains Understanding why they matter Identifying the three types of blockchains Deepening your knowledge of how blockchains work Originally, blockchain was just the computer science term for how to structure and share data. Today blockchains are hailed the “fifth evolution” of computing.
Blockchains are a novel approach to the distributed database. The innovation comes from incorporating old technology in new ways. You can think of blockchains as distributed databases that a group of individuals controls and that store and share information.
There are many different types of blockchains and blockchain applications. Blockchain is an all-encompassing technology that is integrating across platforms and hardware all over the world.
Beginning at the Beginning: What Blockchains Are
A blockchain is a data structure that makes it possible to create a digital ledger of data and share it among a network of independent parties. There are many different types of blockchains.
- Public blockchains: Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin, are large distributed networks that are run through a native cryptocurrency. A cryptocurrency is a unique bit of data that that can be traded between two parties. Public blockchains are open for anyone to participate at any level and have open-source code that their community maintains.
- Permissioned blockchains: Permissioned blockchains, such as Ripple, control roles that individuals can play within the network. They’re still large and distributed systems that use a native token. Their core code may or may not be open source.
- Private blockchains: Private blockchains also known as distributed ledger technology (DLT) tend to be smaller and do not utilize a token or cryptocurrency. Their membership is closely controlled. These types of blockchains are favored by consortiums that have trusted members and trade confidential information.
All three types of blockchains use cryptography to allow each participant on any given network to manage the ledger in a secure way without the need for a central authority to enforce the rules. The removal of central authority from the database structure is one of the most important and powerful aspects of blockchains.
Blockchains create permanent records and histories of transactions, but nothing is really permanent. The permanence of the record is based on the dependability and health of the network. In the context of blockchains, this means that if a large portion of the blockchain community wanted to change information written to their blockchain, they could. Cryptocurrency is used as a reward to incentivize lots of users to facilitate the healthy function of the network through competition. If the records are changed inappropriately, this is known as a 51 percent attack. Small networks with few independent minors are vulnerable because it doesn’t take much effort to change their information, and powerful miners could do so and gain extra cryptocurrency. Ethereum Class experienced just this type of attack.
When data is recorded in a blockchain, it’s extremely difficult to change or remove it. When someone wants to add a record to a blockchain, also called a transaction or an entry, users in the network who have validation control verify the proposed transaction. This is where things get tricky because every blockchain has a slightly different spin on how this works and who can validate a transaction.
What blockchains do
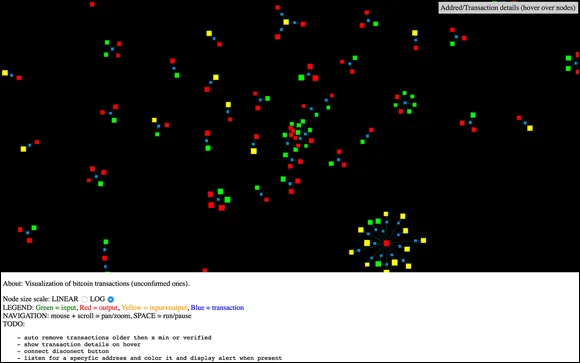
A blockchain is a peer-to-peer system with no central authority managing data flow. One of the key ways to removing central control while maintaining data integrity is to have a large distributed network of independent users. This means that the computers that make up the network are in more than one location. These computers are often referred to as full nodes.
Figure 1-1 shows a visualization of the structure of the Bitcoin blockchain network. You can see it in action at http://dailyblockchain.github.io.
To prevent the network from being corrupted, not only are blockchains decentralized but they often also utilize a cryptocurrency. Blockchain networks produce cryptocurrencies as an incentive to maintain the integrity of the network. Many cryptocurrencies are traded on exchanges like stocks.
Cryptocurrencies work a little differently on each blockchain. Basically, the software pays the hardware to operate. The software is the blockchain protocol. Well-known blockchain protocols include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Bitcoin Cash, Stellar, and EOS. The hardware consists of the full nodes that are securing the data in the network.
Why blockchains matter
Blockchains are recognized as the “fifth evolution” of computing because they’re a new trust layer for the Internet. Before blockchains, trust was established by central authorities that would issue certificates. One you may be familiar with is Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) client certificates. An SSL certificate is the “green lock” that is next to a web domain. It lets you know you’re on a secure website. SSL certificates have proven to not be foolproof. Certificates have been stolen from the domains of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), the U.K.’s Secret Intelligence Service (commonly known as MI6), Microsoft, Yahoo!, Skype, Facebook, and Twitter. Relying on a third party allows for a single point of failure.
Blockchains, on the other hand, establish trust in novel ways. Proof-of-work (POW) blockchains require miners to have a full and accurate history of their transactions to participate on the network. Proof-of-stake (POS) blockchains create trust by requiring nodes that are processing transactions to “st...