
eBook - ePub
Representation Theory of Finite Groups
Martin Burrow
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 208 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Representation Theory of Finite Groups
Martin Burrow
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This volume contains a concise exposition of the theory of finite groups, including the theory of modular representations. The rudiments of linear algebra and knowledge of the elementary concepts of group theory are useful, if not entirely indispensable, prerequisites for reading this book; most of the other requisites, such as the theory of p-adic fields, are developed in the text.
After an introductory chapter on group characters, repression modules, applications of ideas and results from group theory and the regular representation, the author offers penetrating discussions of the representation theory of rings with identity, the representation theory of finite groups, applications of the theory of characters, construction of irreducible representations and modular representations. Well-chosen exercises are included throughout to help students test their understanding of the material. An appendix on groups, rings, ideals, and fields, as well as a bibliography, round out this useful well-thought-out text.
Graduate students wishing to acquire some knowledge of representation theory will find this an excellent text for self-study. The book also lends itself to use as supplementary reading for a course in group theory or in the applications of representation theory to physics.
After an introductory chapter on group characters, repression modules, applications of ideas and results from group theory and the regular representation, the author offers penetrating discussions of the representation theory of rings with identity, the representation theory of finite groups, applications of the theory of characters, construction of irreducible representations and modular representations. Well-chosen exercises are included throughout to help students test their understanding of the material. An appendix on groups, rings, ideals, and fields, as well as a bibliography, round out this useful well-thought-out text.
Graduate students wishing to acquire some knowledge of representation theory will find this an excellent text for self-study. The book also lends itself to use as supplementary reading for a course in group theory or in the applications of representation theory to physics.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Representation Theory of Finite Groups è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Representation Theory of Finite Groups di Martin Burrow in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Mathematics e Group Theory. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MathematicsCategoria
Group TheoryCHAPTER I
Foundations
1. Introduction
Nowadays it is natural for us to think of a group abstractly as a set of elements {a, b, c, ...}, which is closed under an associative multiplication and which permits a solution, for x and y, of any equations: ax = b, and ya = b. On the other hand, we regard a group, which is given in some concrete way, as a realization of an abstract group. This point of view is an inversion of the historical development of group theory which won the abstract concept from particular modes of representation.
Group theory began with finite permutation groups. Any arrangement of n objects in a row is called a permutation of the objects. If we select some arrangement as standard, then any other arrangement can be regarded as achieved from it by an operation of replacements: each object in the standard being replaced by that object which takes its place in the new arrangement. Thus if 123 is standard and 312 is another arrangement, then the replacements are 1 → 3, 2 → 1, and 3 → 2. We write compactly for this operation
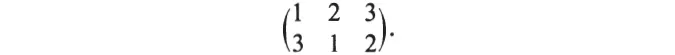
If the replacements of two operations are performed in succession, we get an arrangement which could be achieved directly by a third operation, called the product of the two operations. For example,
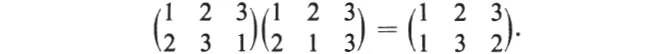
Here we have proceeded from left to right. The product of operations is associative and any set of operations which form a group is a permutation group.
If we have n objects 1, 2, ..., n, then there are n! arrangements and hence n! operations are possible, including the identity:
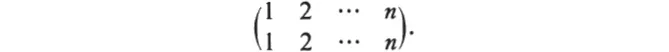
They form a group Sn, the symmetric group on n symbols. Every permutation group on n symbols is a subgroup of Sn. In a remarkable application of a group theory in its infancy Galois showed that every algebraic equation possesses a certain permutation group on whose structure its properties depend.
Cayley discovered the abstract group concept. A theorem of his asserts that every abstract group with a finite number of elements can be realized as a group of permutations of its elements. Thus if G = {a, b, c, ..., g, ...} is the abstract group, then the element of the permutation group P which corresponds to g is the set of replacements a → ag, b → bg, c → cg, ..., or compactly:
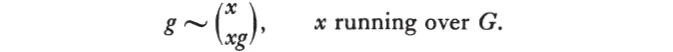
The groups G and P are isomorphic (see Appendix).
A generalization of the permutation group, and the next step historically, is the group of linear substitutions on a finite number of variables. In this case, if the variables are x1, ...,...