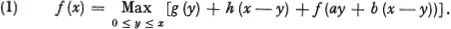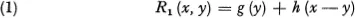![]()
CHAPTER I
A Multi-Stage Allocation Process
§ 1. Introduction
In this chapter we wish to introduce the reader to a representative class of problems lying within the domain of dynamic programming and to the basic approach we shall employ throughout the subsequent pages.
To begin the discussion we shall consider a multi-stage allocation process of rather simple structure which possesses many of the elements common to a variety of processes that occur in mathematical analysis, in such fields as ordinary calculus and the calculus of variations, and in such applied fields as mathematical economics, and in the study of the control of engineering systems.
We shall first formulate the problem in classical terms in order to illustrate some of the difficulties of this straightforward approach. To circumvent these difficulties, we shall then introduce the fundamental approach used throughout the remainder of the book, an approach based upon the idea of imbedding any particular problem within a family of similar problems. This will permit us to replace the original multidimensional maximization problem by the problem of solving a system of recurrence relations involving functions of much smaller dimension.
As an approximation to the solution of this system of functional equations we are lead to a single functional equation, the equation
This equation will be discussed in some detail as far as existence and uniqueness of the solution, properties of the solution, and particular solutions are concerned.
Turning to processes of more complicated type, encompassing a greater range of applications, we shall first discuss time-dependent processes and then derive some multi-dimensional analogues of (1), arising from multi-stage processes requiring a number of decisions at each stage. These multi-dimensional equations give rise to some difficult, and as yet unresolved, questions in computational analysis.
In the concluding portion of the chapter we consider some stochastic versions of these allocation processes. As we shall see, the same analytic methods suffice for the treatment of both stochastic and deterministic processes.
§ 2. A multi-stage allocation process
Let us now proceed to describe a multi-stage allocation process of simple but important type.
Assume that we have a quantity x which we divide into two nonnegative parts, y and x — y, obtaining from the first quantity y a return of g (y) and from the second a return of h (x — y). 1 If we wish to perform this division in such a way as to maximize the total return we are led to the analytic problem of determining the maximum of the function
for all y in the interval [0, x]. Let us assume that g and h are continuous functions of x for all finite x ≥ 0 so that this maximum will always exist.
Consider now a two-stage process. Suppose that as a price for obtaining the return g(y), the original quantity y is reduced to ay, where a is a constant between 0 and 1, 0 ≤ a < 1, and similarly x — y is reduced to b (x — y), 0 ≤ b < 1, as the cost of obtaining h(x — y). With the remaining total, ay + b(x — y), the process is now repeated. We set
for 0 ≤ y1 ≤ x1, and obtain as a result of this new allocation the return g (y1) + h (x1 — y1) at the seco...