
- 384 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Dynamic Programming
About this book
An introduction to the mathematical theory of multistage decision processes, this text takes a "functional equation" approach to the discovery of optimum policies. Written by a leading developer of such policies, it presents a series of methods, uniqueness and existence theorems, and examples for solving the relevant equations. The text examines existence and uniqueness theorems, the optimal inventory equation, bottleneck problems in multistage production processes, a new formalism in the calculus of variation, strategies behind multistage games, and Markovian decision processes. Each chapter concludes with a problem set that Eric V. Denardo of Yale University, in his informative new introduction, calls "a rich lode of applications and research topics." 1957 edition. 37 figures.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER I
A Multi-Stage Allocation Process
§ 1. Introduction
In this chapter we wish to introduce the reader to a representative class of problems lying within the domain of dynamic programming and to the basic approach we shall employ throughout the subsequent pages.
To begin the discussion we shall consider a multi-stage allocation process of rather simple structure which possesses many of the elements common to a variety of processes that occur in mathematical analysis, in such fields as ordinary calculus and the calculus of variations, and in such applied fields as mathematical economics, and in the study of the control of engineering systems.
We shall first formulate the problem in classical terms in order to illustrate some of the difficulties of this straightforward approach. To circumvent these difficulties, we shall then introduce the fundamental approach used throughout the remainder of the book, an approach based upon the idea of imbedding any particular problem within a family of similar problems. This will permit us to replace the original multidimensional maximization problem by the problem of solving a system of recurrence relations involving functions of much smaller dimension.
As an approximation to the solution of this system of functional equations we are lead to a single functional equation, the equation
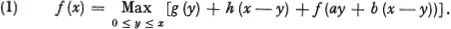
This equation will be discussed in some detail as far as existence and uniqueness of the solution, properties of the solution, and particular solutions are concerned.
Turning to processes of more complicated type, encompassing a greater range of applications, we shall first discuss time-dependent processes and then derive some multi-dimensional analogues of (1), arising from multi-stage processes requiring a number of decisions at each stage. These multi-dimensional equations give rise to some difficult, and as yet unresolved, questions in computational analysis.
In the concluding portion of the chapter we consider some stochastic versions of these allocation processes. As we shall see, the same analytic methods suffice for the treatment of both stochastic and deterministic processes.
§ 2. A multi-stage allocation process
Let us now proceed to describe a multi-stage allocation process of simple but important type.
Assume that we have a quantity x which we divide into two nonnegative parts, y and x — y, obtaining from the first quantity y a return of g (y) and from the second a return of h (x — y). 1 If we wish to perform this division in such a way as to maximize the total return we are led to the analytic problem of determining the maximum of the function
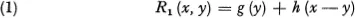
for all y in the interval [0, x]. Let us assume that g and h are continuous functions of x for all finite x ≥ 0 so that this maximum will always exist.
Consider now a two-stage process. Suppose that as a price for obtaining the return g(y), the original quantity y is reduced to ay, where a is a constant between 0 and 1, 0 ≤ a < 1, and similarly x — y is reduced to b (x — y), 0 ≤ b < 1, as the cost of obtaining h(x — y). With the remaining total, ay + b(x — y), the process is now repeated. We set

for 0 ≤ y1 ≤ x1, and obtain as a result of this new allocation the return g (y1) + h (x1 — y1) at the seco...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Introduction to the Dover Edition
- Preface
- Chapter I: A Multi-Stage Allocation Process
- Chapter II: A Stochastic Multi-Stage Decision Process
- Chapter III: The Structure of Dynamic Programming Processes
- Chapter IV: Existence and Uniqueness Theorems
- Chapter V: The Optimal Inventory Equation
- Chapter VI: Bottleneck Problems in Multi-Stage Production Processes
- Chapter VII: Bottleneck Problems: Examples
- Chapter VIII: A Continuous Stochastic Decision Process
- Chapter IX: A New Formalism in the Calculus of Variations
- Chapter X: Multi-Stage Games
- Chapter XI: Markovian Decision Processes
- Index of Applications
- Name and Subject Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Dynamic Programming by Richard Bellman in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Mathematics & Discrete Mathematics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.