
Medical Pharmacology at a Glance
Michael J. Neal
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Medical Pharmacology at a Glance
Michael J. Neal
Informazioni sul libro
The internationally best-selling Medical Pharmacology at a Glance is the ideal companion for all medical and healthcare students, providing a visual overview of pharmacology, and describing the basic principles of drug action, interaction, absorption, and excretion. Clear and accessible chapters organised around common diseases and conditions facilitate efficient clinical learning, and include references to drug classes and side effects, disease pathophysiology, prescribing guidelines, and more.
Now in its ninth edition, this leading guide has been thoroughly updated to reflect current guidelines and drug information. This edition features new and revised illustrations, additional pedagogical tools, and enhanced online content. Widely recognised as both the best introduction to medical pharmacology and the perfect revision tool for USMLE and pharmacology exams, this invaluable guide:
- Covers a wide range of drugs used to treat conditions such as hypertension, anaemias, cancer, and affective disorders
- Explains drug mechanisms and the principles of drug action
- Discusses practical topics including drug misuse, drug indications, and side effects
- Includes a companion website featuring online cases, flashcards, and a list of core drugs
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
1
Introduction: principles of drug action
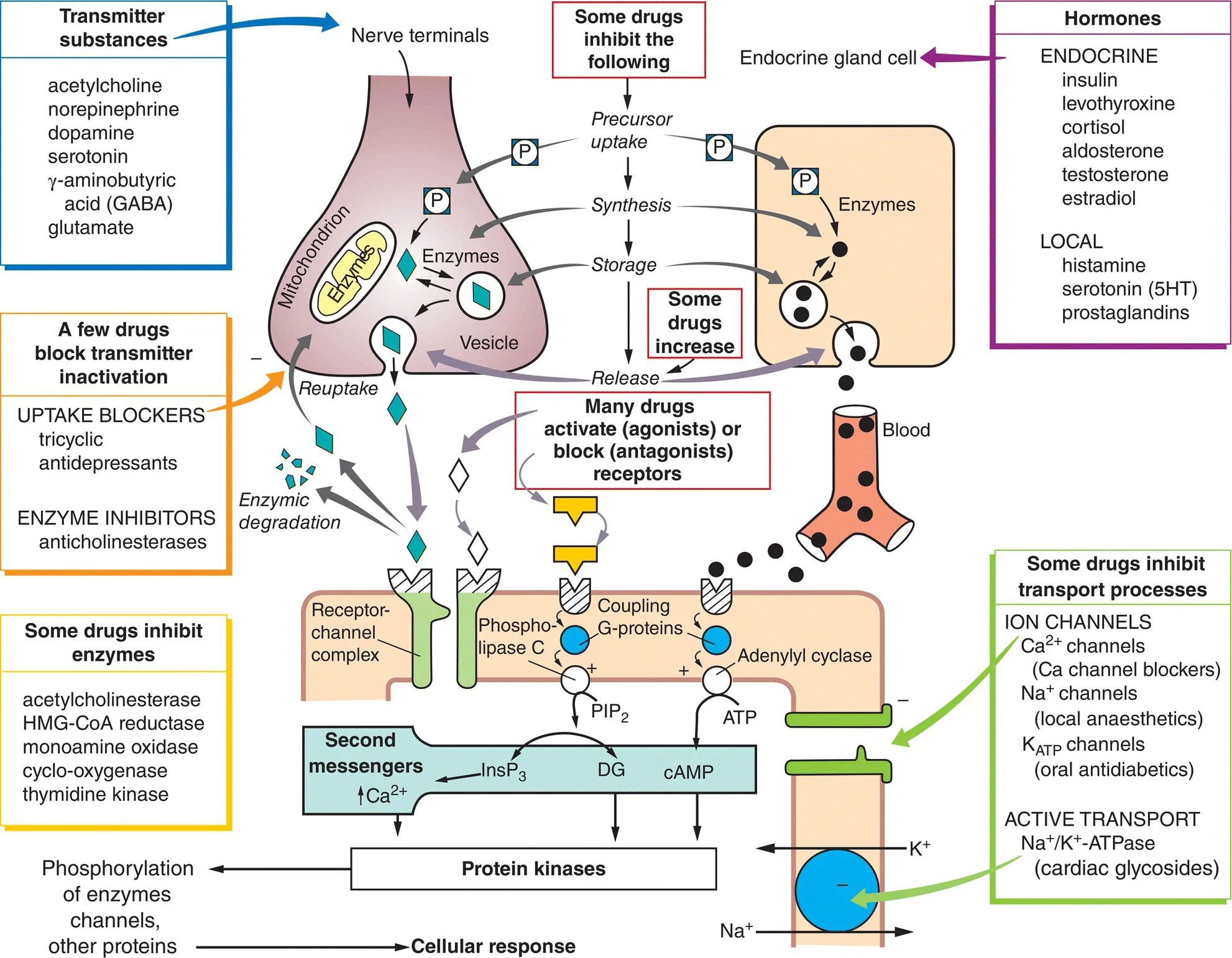
- pharmacodynamics – the effects of the drug on the body; and
- pharmacokinetics – the way the body affects the drug with time (i.e. absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion).



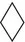


Receptors
- Agonist (ligand)‐gated ion channels are made up of protein subunits that form a central pore (e.g. nicotinic receptor, Chapter 6; γ‐aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, Chapter 24).
- G‐protein‐coupled receptors (see below) form a family of receptors with seven membrane‐spanning helices. They are linked (usually) to physiological responses by second messengers.
- Nuclear receptors for steroid hormones (Chapter 34) and thyroid hormones (Chapter 35) are present in the cell nucleus and regulate transcription and thus protein synthesis.
- Kinase‐linked receptors are surface receptors that possess (usually) intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity. They include receptors for insulin, cytokines and growth factors (Chapter 36).