
eBook - ePub
Designing Microservices using Django
Structuring, Deploying and Managing the Microservices Architecture with Django
Shayank Jain
This is a test
Condividi libro
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Designing Microservices using Django
Structuring, Deploying and Managing the Microservices Architecture with Django
Shayank Jain
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
A step-by-step that will help you build Microservices architecture using Django and Python Key Features
- Understand in-depth the fundamentals of Microservices
- Learn how to create and use Django APIs
- Use web technology such as Nginx, Gunicorn, UWSGI, and Postgresql to deploy a Django project
-
Description
Microservices architectures solve the multiple problems of software architecture. Django is a full-stack development framework, written in python. This book includes everything necessary for web application development; from the user views to the information storage: model, persistence, relationships, controllers, forms, validations, rest API and a very useful back office. Furthermore, the book will show how to build production-ready microservices. It will help you create restful APIs and get familiar with Redis and Celery. Towards the end, the book will show how to secure these services and deploy these microservices using Django. Lastly, it will show how to scale our services. What will you learn
- Understand the basics of Python, Django, and Microservices
- Learn how to deploy Microservices with Django
- Get familiar with Microservices Architecture - Designing, Principles, and Requirements
- Implement Asynchronous task, JWT API Authentication and AWS Serverless with Microservice architecture
-
Who this book is for
This book is for those beginners who want to make their careers in software development. It starts from the basics of python and Django, takes the reader to the Microservices architecture. Table of Contents
1. Basic of Python
2. Major Pillars of OOPS with Python
3. Getting Started with Django
4. API Development with Django
5. Database Modeling with Django
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Designing Microservices using Django è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Designing Microservices using Django di Shayank Jain in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Computer Science e Client-Server Computing. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
Computer ScienceCategoria
Client-Server ComputingCHAPTER 1
Basics of Python
Python is a programming language that lets you work quickly and integrate systems more effectively. It has many applications, such as data analysis, web development, and app development. It has dynamic and strong data type, which can be managed and defined easily.
For microservices, we require basic knowledge of Django. This book is about microservices with Django, and to use Django you should know about Python. Thus, we'll cover the basics of Python in this chapter.
Structure
- Introduction of Python programming language
- Definition of variables, expressions and statements
- Statements
- Operations on strings
- Functions
- Python type conversion functions
- User defined functions
- Execution flow of program
- Scope of the variable
- "if" conditional statement with nested conditions
- The for and while loops
- Advanced data types of Python
- List
- List built-in functions
- Tuple
- Dictionaries
- Dictionaries built-in functions
- Python data type set
- List comprehension
- Iterators and generators
- Additional – PEP8 style guide for Python code
Objective
This chapter covers all the basic concepts of Python and these are enough to understand Django. At the end of this chapter, you can easily understand variable definition, functions, statements, advance data type, code blocks, flow of the program and coding standard. All the topics are covered with real life examples and executable code.
Introduction of Python programming language
You must have heard about many programming languages, Python is one of them.
Python is one of the dynamic programming languages compared to other languages such as Java, Perl, PHP, and Ruby. It is often termed as a scripting language. It provides support for automatic memory management, multiple programming paradigms, and implements the basic concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP). Python executes its code line by line, thus it is known as an interpreter language.
The interpreter functionality lets it read a program and execute one line at a time.
The following image shows the steps of Python code compilation:
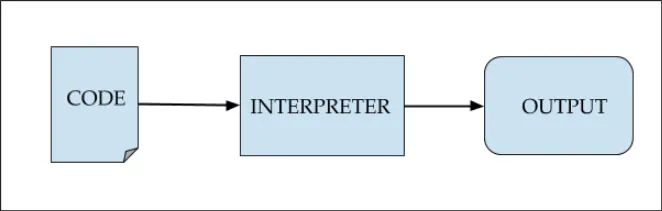
Figure 1.1: Python code compilation steps
Python code can be executed in two ways, one we can open the Python console (command-line mode) and write our code line by line, which executes the code line by line. The second way is to put all your code into a single file then execute the script. The following example shows how command-line mode works, you type the programs then interpreter prints the result:
$ pythonPython 3.5.2 (default, Nov 12 2018, 13:43:14)[GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linuxType "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.>>> print("Welcome to Python World!!!!")Welcome to Python World!!!!In the above command, Python command starts the Python console application. The next two lines contain the start messages, which is the default start message from the Python interpreter. The next line starts with
>>>, it is the prompt that indicates it is ready. We write print ("Welcome to Python World!!!!"), and the interpreter replies Welcome to Python World!!!!.Alternatively, we can write a program inside a file and execute the file. That file is called a script. For example, we create a file
first_python_script.py with the following code:print( "Welcome to Python World!!!!" )As per convention, the names of files which contain Python should end with .
py. To execute the program, we have to tell the interpreter the name of the script:$ python first_python_script.pyWelcome to Python World!!!!Definition of variables, expressions, and statements
As we know, Python is a dynamic programming language. Compared to other languages like C, C++ or Java, In Python, we are not bound to define data type at the time of defining any variable. Please refer to the examples mentioned below:
- Let's take an example of string definition:
>>> a = "Hello Shayank">>> type(a)<class 'str'>>>> print(a)Hello Shayank - Let's take an example of integer definition:
>>> a = 5>>> type(a)<class 'int'>>>> print(a)5 - Let's take an example of float definition:
>>> a = 5.0>>> type(a)<class 'float'>>>> print(a)5.0 - Let's take an example of Boolean definition:
>>> a = True>>> type(a)<class 'bool'>>>> print(a)True
In the above mentioned examples,
type() method is used. It is a built-in method in Python, which is used to know the data type of the variable. The syntax is type(variable) as mentioned in the above example.There are few ways in Python which are not allowed to define the variable; if we use these ways, it will throw a syntax error:
>>> 09var = "program" File "<stdin>", line 109var = "program"^SyntaxError: invalid syntax>>> variable$ = 1000000File "<stdin>", line 1variable$ = 1000000^SyntaxError: invalid syntax>>> class = "test hello"File "<stdin>", line 1class = "test hello"^SyntaxError: invalid syntax09var is not allowed because the variable name does not start with a letter. variable$ is gives an error because it contains the special symbol, that dollar sign. But you may be thinking why not class?It is through error because the class belongs to the Python keywords list. Keywords are sp...