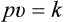Introduction to Medical Laboratory Technology
F. J. Baker,R. E. Silverton
- 746 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Introduction to Medical Laboratory Technology
F. J. Baker,R. E. Silverton
Informazioni sul libro
Introduction to Medical Laboratory Technology presents the development in the medical laboratory science. It discusses the general laboratory glassware and apparatus. It addresses a more specialized procedure in mechanization, automation, and data processing. Some of the topics covered in the book are the composition of glass; cleaning of glassware; the technique of using volumetric pipettes; technique for centrifugation; the production of chemically pure water; principal foci of a converging lens; micrometry; magnification; setting up the microscope; and fluorescence microscopy. The precautions against infection are covered. The storage of chemicals and treatment of accidents are discussed. The text describes the collection and reporting of specimens. A study of the fundamentals of chemistry and endocrine systems is presented. A chapter is devoted to the elementary colorimetry and spectro-photometry. Another section focuses on the introduction to clinical chemistry and blood gas analysis. The book can provide useful information to scientists, physicists, doctors, students, and researchers.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Some Fundamentals of Chemistry
Publisher Summary
1 Law of Conservation of Mass
2 Law of Constant Composition
3 Law of Multiple Proportions
4 Law of Reciprocal Proportions (or equivalent proportions)
Equivalents
THE GAS LAWS
1 Boyle’s Law