
eBook - ePub
Sustainable Manufacturing
Concepts, Tools, Methods and Case Studies
S. Vinodh
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 126 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Sustainable Manufacturing
Concepts, Tools, Methods and Case Studies
S. Vinodh
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
Sustainability enables the development of products with minimal environment impact coupled with economical and societal benefits. This book provides an understanding of theoretical and practical perspectives pertaining to Sustainable manufacturing.This book focuses on fundamentals, providing insights, concepts, tools, methods, case studies, and practical perspectives taken from research.The book will be of interest to students, researchers and industry practitioners.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Sustainable Manufacturing è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Sustainable Manufacturing di S. Vinodh in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Technik & Maschinenbau e Maschinen- und Anlagebau. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
1
Concepts and Fundamentals of Sustainable Manufacturing, Triple Bottom Line Approach
1.1 Overview of Triple Bottom Line
Triple bottom line (TBL) is the base for sustainability. TBL underlies the rationale of sustainability by evaluating the impact in terms of profitability; shareholder values; and its societal, people and environmental capital (Savitz, 2013). It is based on 3Ps: profitability, people and planet. Profitability pertains to the economy; people pertain to societal and planet pertains to environmental dimensions. It considers the development and application of a corporate strategy involving environmental, societal and financial results (Mowat, 2002). TBL provides a three-dimensional view of sustainability moving from the viewpoint of the environment to include economic and societal dimensions (Shaffer, 2018). Widely cited definitions of TBL are presented in Table 1.1.
TABLE 1.1
Widely Cited Definitions of TBL
Widely Cited Definitions of TBL
Definition | Reference |
‘Taking environmental, social and financial results into consideration in the development and implementation of a corporate business strategy’. | Mowat (2002) |
TBL firms aim to become more responsive ecologically and socially while prospering economically. This threefold focus is often referred to in terms of ‘people, planet, profit’, or as the ‘‘triple bottom line’ (TBL). | Elkington (1997) |
1.2 Overview of Sustainable Manufacturing with Evolutionary Aspects
Manufacturing systems have witnessed a shift from mass production to lean, green and sustainable manufacturing. The transition of manufacturing systems is shown in Figure 1.1. Key parameters governing this transition include product complexity, market dynamism and stakeholder value. Craft manufacturing includes skilled employees and has low production volume. Mass manufacturing is characterized by interchangeable parts and delivers high productivity (Rojko, 2017). It can handle market dynamism better than a craft system. Mass manufacturing is characterized by high-volume manufacturing with limited product variants. It fulfils economies of scale, which state that the unit cost of a product comes down as a result of high-volume production. Lean manufacturing is characterized by waste elimination, streamlined processes and value addition (de Freitas et al., 2017). Lean is a predecessor manufacturing system to green and sustainable manufacturing. Lean production is based on the Toyota Production System (TPS), which is waste reduction based on skilled workers and focused on value addition. Green manufacturing is environmentally benign and 3R-based (reduce, reuse, recycle). Sustainable manufacturing is innovative and 6R-based (3Rs plus recovery, redesign and remanufacture). Sustainable manufacturing is referred to as an ‘E’ paradigm with the focus on ecology, economy, excellence and so on. Lean is a predecessor element to sustainability as lean facilitates waste elimination, which forms the path for sustainable manufacturing.
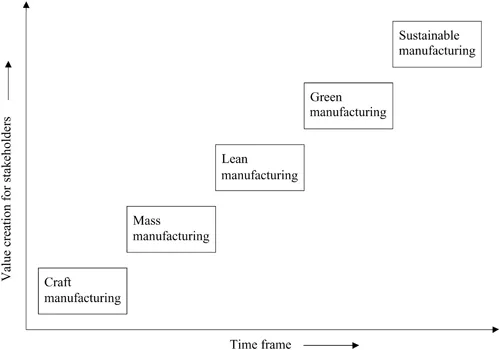
Transition of manufacturing systems.
Sustainable manufacturing (SM) is concerned with executing a new form of business with value creation to develop green products and processes in demand (Alayón, 2016). Key business benefits from SM include improvement of efficiency and productivity, reduced usage of hazardous materials, compliance with regulations, enhanced reputation and enhanced community relations.
The environmental focus of manufacturing was initially on pollution abatement (reducing pollution). Then the shift was towards cleaner production and pollution prevention (U.S. Department of Commerce, 2011).
1.2.1 Evolution of Sustainable Manufacturing
The main environmental focus in a manufacturing context had been referred to as pollution abatement, that is preventing the pollution generated from entering the environment. Then the focus became cleaner production and pollution prevention. With cleaner production, there exists scope for cost reduction and other economic advantages (U.S. Department of Commerce, 2011).
- Clean technologies are vital from the viewpoint of sustainable manufacturing and include associated aspects such as environmental protection, compliance with regulatory bodies, pollution prevention and renewable technologies.
- Green production deals with development of green products, i.e. products with minimal environmental impact.
- Sustainable manufacturing includes a methodological approach for waste elimination by resource optimization and utilization of resources, and technologies with less environmental impact.
1.3 Definitions of Sustainable Manufacturing
Widely cited definitions of sustainable manufacturing are presented in Table 1.2. Elements identified with sustainable manufacturing include fewer environmental impacts, resources conservation, safety, economic benefits, meeting requirements of future generations, energy conservation, employee health, inclusive growth and optimal resource utilization. SM facilitates the development of green products that are designed to reduce environmental impact with the usage of recyclable materials.
TABLE 1.2
Widely Cited Definitions of Sustainable Manufacturing
Widely Cited Definitions of Sustainable Manufacturing
Definition | Reference |
‘Manufacturing processes that meet the needs of the present without compromising future generations’ ability to meet their own needs’. | Gardner and Colwill (2016) |
‘The creation of manufactured products that use processes that minimize negative environmental impacts, conserve energy and natural resources, are safe for employees, communities, and consumers; and are economically sound’. | U.S. Department of Commerce (2011) |
1.3.1 Business Benefits of SM are (Alayon, 2016)
- Increased sales.
- Improved efficiency and productivity.
- Compliance with regulations.
- Enhanced reputation and image.
- Better community relations (Alayón, 2016).
1.3.2 Implementation of Sustainable Manufacturing at Initial Stage
The details of implementing SM are presented as follows (U.S. Department of Commerce, 2011; Kishawy et al., 2018):
- Housekeeping – Can be facilitated with 5S lean tools for enhancement in work practices.
- Process optimi...