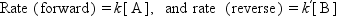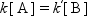A concise introduction is given to the fundamental knowledge required to understand the heterogeneous catalysis of mixed oxides and to the concept of catalyst design. The fundamental knowledge includes the rate versus equilibrium relation; rate equation; the mechanism of catalytic reaction; essential functions of a catalyst, namely, activity, selectivity, and durability (or life); and catalytic reaction engineering such as mass and heat transfer. Typical methods for the preparation and characterization of catalysts and for the elucidation of the reaction mechanism, as well as a short history of industrial catalysts, are also provided.
Fundamental concepts and principles indispensable to understand the heterogeneous catalysis of mixed oxides are described in this chapter [1].
1.1 Catalyst and Catalysis
Catalyst is a substance that is present in a small amount in the reaction system and accelerates the desired chemical reaction(s), but little changes during the reaction. Catalysis is a general term for the function of catalyst. Almost all materials and goods that are daily used are produced through catalytic processes from various raw materials.
Many high-performance catalysts are used, in order to utilize efficiently raw materials, including recycling of used materials, and to utilize efficiently the existing as well as “new” energy sources. Catalysts are used not only for chemical synthetic processes but also for other uses such as electrodes of fuel cells and batteries. In addition, catalysts are used to protect and improve the environment. The latter catalysts are called environmental catalysts, that is, “Kankyou Shokubai” in Japanese which is a new word first used by the author in the late 1970s.
1.1.1 Rate and Equilibrium of Chemical Reaction and Role of Catalyst
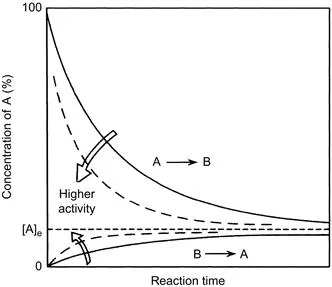
A catalyst changes (accelerates in most cases) the rate of chemical reactions to approach the equilibrium but does not change the equilibrium itself. It is important to distinguish between the kinetics (rate of reaction) and thermodynamics (equilibrium constant of reaction). The difference may be evident in Fig. 1.1, which schematically shows the case of a simple reversible reaction of A ↔ B. The rate to approach the equilibrium composition changes from a catalyst to another, but the equilibrium finally attained is the same. If the forward and reverse reactions are first order, the rates are expressed by Eq. (1.1) as
Figure 1.1 Time course of a reversible reaction, A ↔ B. The concentration reaches faster the equilibrium concentration [A]e over a catalyst with a higher activity, but the equilibrium concentration is the same.
At the equilibrium, the rates of forward and reverse reactions are identical, then,
where the ratio of [B]/[A] is being determined by the equilibrium constant, K = k/k′. With an active catalyst, the rate to approach the equilibrium is fast, and for a less active catalyst it is slower. Therefore, both forward and reverse reactions are faster over a more active catalyst at the equilibrium, while both rates are identical for each case.
1.1.2 Three Essential Functions of Catalyst
Catalytic activity, selectivity, and durability (= catalyst life) are the three most important functions of catalyst.
Activity is most fundamental. A reaction which does not occur in the absence of catalyst could proceed in the presence of catalyst. With a more active catalyst, the production rate per volume of reactor becomes larger and the reactor volume can be made smaller.
Selectivity is the most interesting and attractive function of catalyst, which selects one (or more) desirable reaction(s) among many reactions that would possibly occur. Choosing a reaction which produces a thermodynamically unfavorable but valuable product is one of the most attractive functions of catalyst. A fascinating function of catalyst is stereoselectivity that produces one of the two stereoisomers which have thermodynamically the same stability.
The selectivity may be divided into two categories (Eq. 1.3). One is to select one product among several possible products starting from one reacting molecule, e.g., choosing only A to B (Eq. 1.3a). This may be called (a) product-selectivity. Another type is to select one reactant in a mixture of several reactants choosing A from a mixture of A and B (Eq. 1.3...