
Interpretable Machine Learning with Python
Learn to build interpretable high-performance models with hands-on real-world examples
Serg Masís
- 736 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Interpretable Machine Learning with Python
Learn to build interpretable high-performance models with hands-on real-world examples
Serg Masís
Informazioni sul libro
A deep and detailed dive into the key aspects and challenges of machine learning interpretability, complete with the know-how on how to overcome and leverage them to build fairer, safer, and more reliable models
Key Features
- Learn how to extract easy-to-understand insights from any machine learning model
- Become well-versed with interpretability techniques to build fairer, safer, and more reliable models
- Mitigate risks in AI systems before they have broader implications by learning how to debug black-box models
Book Description
Do you want to gain a deeper understanding of your models and better mitigate poor prediction risks associated with machine learning interpretation? If so, then Interpretable Machine Learning with Python deserves a place on your bookshelf.We'll be starting off with the fundamentals of interpretability, its relevance in business, and exploring its key aspects and challenges. As you progress through the chapters, you'll then focus on how white-box models work, compare them to black-box and glass-box models, and examine their trade-off. You'll also get you up to speed with a vast array of interpretation methods, also known as Explainable AI (XAI) methods, and how to apply them to different use cases, be it for classification or regression, for tabular, time-series, image or text. In addition to the step-by-step code, this book will also help you interpret model outcomes using examples. You'll get hands-on with tuning models and training data for interpretability by reducing complexity, mitigating bias, placing guardrails, and enhancing reliability. The methods you'll explore here range from state-of-the-art feature selection and dataset debiasing methods to monotonic constraints and adversarial retraining.By the end of this book, you'll be able to understand ML models better and enhance them through interpretability tuning.
What you will learn
- Recognize the importance of interpretability in business
- Study models that are intrinsically interpretable such as linear models, decision trees, and Naïve Bayes
- Become well-versed in interpreting models with model-agnostic methods
- Visualize how an image classifier works and what it learns
- Understand how to mitigate the influence of bias in datasets
- Discover how to make models more reliable with adversarial robustness
- Use monotonic constraints to make fairer and safer models
Who this book is for
This book is primarily written for data scientists, machine learning developers, and data stewards who find themselves under increasing pressures to explain the workings of AI systems, their impacts on decision making, and how they identify and manage bias. It's also a useful resource for self-taught ML enthusiasts and beginners who want to go deeper into the subject matter, though a solid grasp on the Python programming language and ML fundamentals is needed to follow along.
]]>
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Section 1: Introduction to Machine Learning Interpretation
- Chapter 1, Interpretation, Interpretability and Explainability; and why does it all matter?
- Chapter 2, Key Concepts of Interpretability
- Chapter 3, Interpretation Challenges
Chapter 1: Interpretation, Interpretability, and Explainability; and Why Does It All Matter?
- What is machine learning interpretation?
- Understanding the difference between interpretation and explainability
- A business case for interpretability
Technical requirements
What is machine learning interpretation?
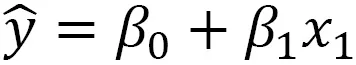

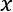
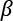
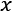
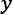
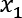
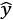
Understanding a simple weight prediction model
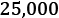
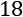
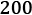

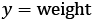
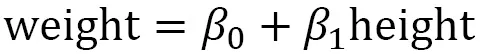
- requests to fetch the web page
- bs4 (Beautiful Soup) to scrape the table from the web page
- pandas to load the table in to a dataframe
- sklearn (scikit-learn) to fit the linear regression model and calculate its error
- matplotlib to visualize the model
- scipy to test the correlation