eBook - ePub
Decentralization, Local Governance, and Local Economic Development in Mongolia
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 92 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Decentralization, Local Governance, and Local Economic Development in Mongolia
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This publication presents an empirical assessment of Mongolia's system of decentralized governance and the extent to which it translates into the actual and practical working environment for subnational and local governments. It focuses on the roles of subnational and local governments in providing public services and promoting local economic development.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Decentralization, Local Governance, and Local Economic Development in Mongolia è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Decentralization, Local Governance, and Local Economic Development in Mongolia di in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Law e Public Law. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
LawCategoria
Public LawSUBNATIONAL GOVERNANCE AND SERVICE DELIVERY IN PRACTICE
This section explores how SNGs manage their primary levers of local public action, the delivery of the range of socioeconomic infrastructure and services for which they are responsible, and the constraints and issues that surround this.
A. Service Delivery Spending Responsibilities
1. Legal Mandates
Since 2012, there has been a degree of expenditure responsibility assigned to SNGs under the Budget Law (2012):
(i)Under Article 58, there is a set of modest, devolved service delivery functions of aimags and soums.
(ii)Under Articles 39.1 and 61.1, there is delegation of responsibilities for basic education, primary health care, social welfare, physical fitness, and culture to SNGs. These are funded through special-purpose fiscal transfers. In the most recent Budget Law revision, from 2019 some minor spending functions related to physical fitness, culture, and parts of school and clinic operating budgets will no longer be transferred to SNGs as devolved functions and funded from the base expenditure budget (Table 4).
Table 4: Functions Decentralized under the Budget Law
Sector | Aimags and Capital City | Soums and Districts |
Main Functions Devolved (Budget Law, Article 58) | ||
Social Welfare | • Social care and welfare (upon a decision of SNG governors) • Playgrounds | • Social care and welfare (upon a decision of SNG governors) • Playgrounds |
Transport, Roads | • Public transport • Aimag and Inter-soum roads • Street lighting | • Street lighting maintenance |
Water and Sanitation | • Water supply • Sewerage, drainage • Waste removal • Public hygiene | • Public hygiene, street cleaning, waste removal |
Agriculture and Livestock | • Livestock restocking • Pasture management • Pest control | • Livestock restocking • Pasture management |
Economic Development | • O&M electric distribution network • Development of small and medium-sized enterprises | |
Environment | • Environmental protection and rehabilitation • Flood protection | • Environmental protection |
Capital Infrastructure | • Urban planning, construction of new infrastructure • Maintenance of locally owned buildings | |
Main functions delegated (Budget Law, Articles 39.1 and 61.1) | ||
Education | • Preschool, general education, fitness, and culture | • Preschool, general education, fitness, and culture |
Health | • Primary health care | • Primary health care |
Social Welfare | • Child protection and development | • Child protection and development |
O&M = operation and maintenance, SNG = subnational government.
Source: Asian Development Bank (compiled from the Budget Law of Mongolia, 2010).
However, these are recurrent budget responsibilities for which all local spending is subject to rigid central budget norms, greatly limiting any local choice.
Despite the provisions noted in Table 4, in practice, capital budget spending is still controlled by the central sector ministries. The main resource for local capital budget spending is the LDF transfer and for which there are menus for aimags and soums, although these are not always clear. For example, it is not clear if these menus are exclusive mandates for spending only to be undertaken by SNGs or permissive lists of allowable spending that the central government may decide to spend.
A review process of SNG functional assignments has been launched by the Cabinet Secretariat under the SDC-supported Decentralisation Policy Support Program. A methodology has been developed with initial piloting undertaken in the Ministry of Environment, which is now being extended to the Ministry of Construction and Urban Development and the Ministry of Labour. The next step will be to assess SNG capacity to adopt new functions.
The Cabinet Secretariat officially endorsed this methodology in a January 2018 circular to all ministries. The recent Budget Law revision included a provision under Article 58 that each ministry should review SNG assignments every 3 to 5 years. However, based on international experience, it remains to be seen how enthusiastically line ministries will move to cede to SNGs any control over their responsibilities and the associated budgetary and staff resources.
The Budget Law is not the only statute mandating functions to SNGs. Functions are scattered throughout other laws and regulations and not always aligned or updated and constitute a source of some confusion (Box 10).
Box 10: Unclear Mandates to Subnational Governments
In 2014, Ulaanbaatar City authorities undertook an extensive review of service delivery functions, roles, and procedures as laid down under the law. The findings were revealing.
(i)A large number of legal and regulatory instruments (137) in one way or another dictate service responsibilities to city authorities at one level or another.
(ii)A large number of service delivery responsibilities (536) are mandated to city, district, and khoroo (urban ward) authorities. For example:
• roads and related infrastructure maintenance: 34 responsibilities
• social policy: 75 responsibilities
• social protection and welfare: 122 responsibilities
• public order: 23 responsibilities
• environment: 29 responsibilities
(iii)A large degree of confusion existed across this range of responsibilities. Among the 536 distinct service responsibilities, there were 147 overlaps or conflicts in mandated responsibilities between city and districts, or districts and khoroos.
A similar review conducted by another aimag (province) counted 80 sector-specific laws or regulations that in different ways specify subnational government service delivery responsibilities.
Source: Consultations with Ulaanbaatar City officials.
2. Spending Patterns in Practice
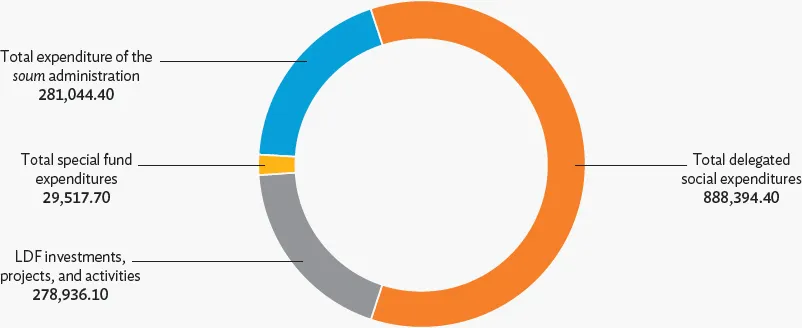
Overall, subnational spending in 2017 constituted 26% of all national government spending, down from 29% in 2014 (Figure 3).
No national budget data on SNG spending by sector were available other than for Ulaanbaatar (Appendix 1). Based on field visits, it appears that the bulk of this spending is on the functions delegated to SNGs under Articles 39 and 61 (education, health, and social welfare), accounting for 60% of the budget. Most SNG revenues compri...