![]()
PART ONE : OUTSIDE THE BUILDING
Chapter 1
WASTEWATER DRAINAGE SYSTEMS
This chapter discusses the evolution of site-based and municipal drainage systems and the importance of good drainage for public health and well-being. It also highlights the importance of good drainage design and the choice of appropriate methods for achieving both water efficiency and resilience. The second part of the chapter will present the main terminology, criteria and factors that inform ‘traditional’ drainage design in and around buildings and the built environment.
Here, building drainage system types and design considerations are discussed with particular focus on the collection and transmission of rainwater, foul and wastewater from buildings; commonly referred to as sewer systems. In the UK, sewer systems can be private and public, or separate and combined.
Useful standards and guidance documents include:
•BS EN 752 (2017) Drain and sewer systems outside buildings. Sewer system management (formerly seven parts, now only one part)
•BS EN 12056 Part 3 Gravity drainage systems inside buildings – Roof drainage, layout and calculation (although title is for ‘inside buildings’ the scope includes rainwater drainage attached to a building)
•EN 16933-2 (2018) Drain and sewer systems outside buildings – Design Part 2: Hydraulic design
•BS EN 1610 Construction and testing of drains and sewers
•BS EN 16932-1 (2018) Drain and sewer systems outside buildings. Pumping systems (In 3 parts including Vacuum systems and Positive pressure systems)
•BS EN 295 (2013) Vitrified clay pipe systems for drains and sewers (Currently in seven parts)
•BS 65 (1991) Specification for vitrified clay pipes, fittings and ducts, flexible mechanical joints for use solely with surface water pipes and fittings
•BS 4660 (2000) Thermoplastics ancillary fittings of nominal sizes 110 and 160 for below-ground gravity drainage and sewerage
•CIBSE Guide G (current version): Public Health & Plumbing Engineering.
The EN 752 is a particularly useful reference. It includes a helpful diagram of the various drainage systems that will be found in a typical urban water catchment e.g. river basin. It shows how the different systems are interconnected and can all impact on local water bodies. It differs from previous drain and sewer standards in that environmental issues are foremost and reference is now given to important European directives such as the:
•EU Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive (91/271/EEC)
•EU Bathing Waters Directive (2006/7/EC)
•EU Groundwater Directive (2006/118/EC)
•EU Shellfish Waters Directive (2006/113/EC), and the
•EU Floods Directive (2007/60/EC).
Although the design of a drain or sewer system needs to take into account the anticipated loading, EN 752 also now requires the design to be future-proof by making provisions for:
•increased flows due to new developments;
•reduced flows due to changes in the development and changes in water use;
•increased flows resulting from changes to existing developments;
•reduced hydraulic capacity resulting from increased hydraulic pipeline roughness (e.g. due to deterioration) in the drains or sewers or wear in pumps;
•reduced hydraulic capacity due to build-up of sediments in sewers.
Private and Public Sewer Systems
Generally, when drains and sewers are given ownership (private or public), this means that they are piped conduits. Although the terms public and private drains and sewers are used around the world, they can have very different practical and legal meanings. Drains and sewers may be installed in the wealthier parts of the towns if treatment facilities have been developed and there are continuous water supplies, but installations in poorer areas may be limited by water supplies, topography and the high densities of population. In areas where pit latrines predominate, sewerage systems are less common. In such situations, a drain may simply be a ditch and to a nearby water body, e.g. a river.
A private sewer system consists of drainage situated within the boundary of private land or property. This means that the land or property owner is responsible for repair and maintenance. A private sewer can serve multiple housing units, e.g. apartments or buildings within the private boundary whose system of drains then combine to single outlet to a public sewer system.
Public or adopted sewers refers to drains and pipelines outside the property boundary. These are maintained by the local authority or municipality. In England and Wales, The Water Industry (Schemes for Adoption of Private Sewers) Regulations 2011 states that with some exceptions, all privately owned sewers and lateral drains (see definitions) that communicate with or drains to an existing public sewer as at 1 July 2011 will become the responsibility of the sewerage undertaker – normally the water and sewerage company for the area. However, property owners will still be responsible for the sections of pipe between their property/building and the transferred private sewer or lateral drain. This rule also applies to surface water sewers except those that drain to a water body or outlet other than the public sewer (see Fig. 1.1).
Fig. 1.1 Private Sewer Adoption since 2011. (Adapted from: Defra (2011) The Private Sewer Transfer Regulations: Provisional non-statutory guidance on private sewers transfer regulations. Crown Copyright. June 2011)
Separate and Combined Sewer Systems
Drainage systems consist of above and below-ground networks of pipes designed to convey foul, surface and rainwater to the sewers. These are typically situated to run alongside or under road networks. The below-ground drainage systems can be separate or combined.
A separate drainage system involves using one sewer system to remove rainwater collected from the roof and other surfaces to a public sewer network, and another to remove the foul and wastewater to a different public sewer network. BS EN 1085:2007 Wastewater Treatment Vocabulary [definition 2120] defines it as two pipelines, one carrying foul wastewater and the other surface water.
A combined system is where both the rain and foul water are removed via the same public sewer network. Historically and pre-1920s in the UK, a combined sewer was more common. However, there are advantages to a separate sewer system that includes: managing rainwater peak flow – reducing the risks of overflows and backflows of the system; reducing treatment loads since surface water is less contaminated than foul water; and reducing the risk of sewage contamination of water bodies. The situation in most other industrialized countries around the world is similar. Some places, such as Washington in the USA, have tried to separate existing combined sewers, but the cost and disruption is very high.
The trend towards separated systems with sewer systems has increased over the last few decades, as there are more concerns over discharges from combined sewer overflows (CSOs) and a general desire to treat foul water separately to stormwater. However, there is less prevalence of separate drainage systems within buildings, where greywater and blackwater could be separated, as the cleansing effect of flushes from WCs (blackwater) helps to minimize the deposits from surfactant using appliances such as sinks, baths and showers.
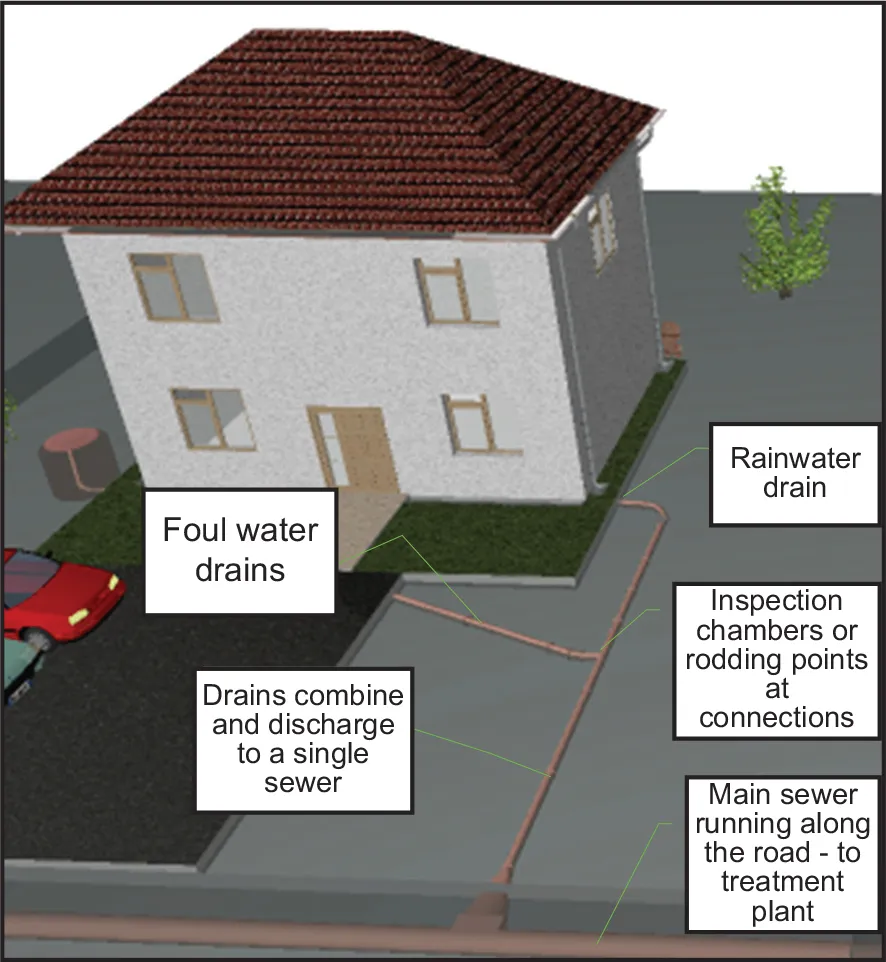
Fig. 1.2a Combined drainage systems.
Fig. 1.2b Different options for separate drainage systems.
However, although combined systems can be connected together below ground, many systems exist where rainwater and foul water are combined above ground; for instance using hoppers or branch connections.
Other Drainage Systems
The current...