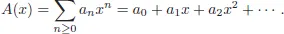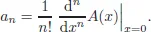Algebra, Logic and Combinatorics
Shaun Bullett, Tom Fearn;Frank Smith
- 184 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Algebra, Logic and Combinatorics
Shaun Bullett, Tom Fearn;Frank Smith
Informazioni sul libro
This book leads readers from a basic foundation to an advanced level understanding of algebra, logic and combinatorics. Perfect for graduate or PhD mathematical-science students looking for help in understanding the fundamentals of the topic, it also explores more specific areas such as invariant theory of finite groups, model theory, and enumerative combinatorics.
Algebra, Logic and Combinatorics is the third volume of the LTCC Advanced Mathematics Series. This series is the first to provide advanced introductions to mathematical science topics to advanced students of mathematics. Edited by the three joint heads of the London Taught Course Centre for PhD Students in the Mathematical Sciences (LTCC), each book supports readers in broadening their mathematical knowledge outside of their immediate research disciplines while also covering specialized key areas.
Contents:
- Enumerative Combinatorics (Peter J Cameron)
- Introduction to the Finite Simple Groups (Robert A Wilson)
- Introduction to Representations of Algebras and Quivers (Anton Cox)
- The Invariant Theory of Finite Groups (P Fleischmann and R J Shank)
- Model Theory (I Tomašić)
Readership: Researchers, graduate or PhD mathematical-science students who require a reference book that covers algebra, logic or combinatorics.
Pure Mathematics;Applied Mathematics;Mathematical Sciences;Techniques;Algebra;Logic;Combinatorics;Fluid Dynamics;Solid Mechanics Key Features:
- Each chapter is written by a leading lecturer in the field
- Concise and versatile
- Can be used as a masters level teaching support or a reference handbook for researchers
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Chapter 1
Enumerative Combinatorics
Queen Mary University of London, London E1 4NS, UK∗
[email protected]
1.Introduction
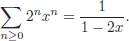
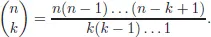
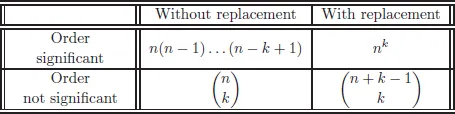
2.Formal Power Series
2.1.Definition