An Elementary Approach to Design and Analysis of Algorithms
Lekh Raj Vermani, Shalini Vermani
- 536 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
An Elementary Approach to Design and Analysis of Algorithms
Lekh Raj Vermani, Shalini Vermani
Informazioni sul libro
In computer science, an algorithm is an unambiguous specification of how to solve a class of problems. Algorithms can perform calculation, data processing and automated reasoning tasks.
As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function. Starting from an initial state and initial input (perhaps empty), the instructions describe a computation that, when executed, proceeds through a finite number of well-defined successive states, eventually producing 'output' and terminating at a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate random input.
This book introduces a set of concepts in solving problems computationally such as Growth of Functions; Backtracking; Divide and Conquer; Greedy Algorithms; Dynamic Programming; Elementary Graph Algorithms; Minimal Spanning Tree; Single-Source Shortest Paths; All Pairs Shortest Paths; Flow Networks; Polynomial Multiplication, to ways of solving NP-Complete Problems, supported with comprehensive, and detailed problems and solutions, making it an ideal resource to those studying computer science, computer engineering and information technology.
Contents:
- Preface
- About the Authors
- Algorithms
- Growth of Functions
- Backtracking
- Divide and Conquer
- Greedy Algorithms
- Dynamic Programming
- Elementary Graph Algorithms
- Minimal Spanning Tree
- Single-Source Shortest Paths
- All Pairs Shortest Paths
- Flow Networks
- Polynomial Multiplication, FFT and DFT
- String Matching
- Sorting Networks
- NP-Complete Problems
- Bibliography
- Index
Readership: Students studying for degrees in computer science, computer engineering and information technology.Algorithms;Computer Science;Computer Engineering;Information Technology00
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Chapter 1
Algorithms
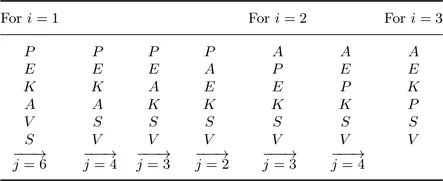
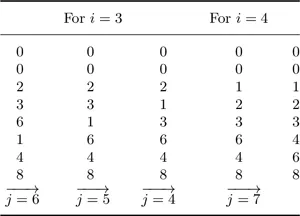
1.1.Some Sorting Algorithms

1.1.1.Bubble sort