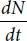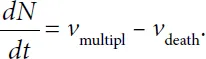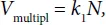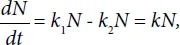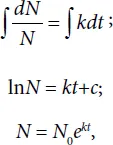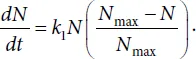![]()
Chapter 1
Dynamic Properties of Biological Processes
Biological Kinetics. Intricate network of various reactions, specifically organized in time and space, underlie both cell exchange processes with the environment and internal metabolism. In biological systems, components interact continuously with each other, which for the most part specifies the nature of dynamic behavior of intact biological systems, mechanisms of their self-control and governing named kinetics of biological processes. As a result of such processes, concentrations of different substances, the number of individual cells and the biomass of organisms change; the other values may also vary, for instance the transmembrane potential in the cell. Upon description of the kinetics in biological systems, the basic initial prerequisites are generally the same as in chemical kinetics.
It is believed that changes of variables at every time moment can be described using corresponding differential equations. In addition to variable values, a kinetic system has a set of specific parameters that remain unchanged during its examination and characterize the conditions of reactions (temperature, humidity, pH, and electrostatic conductivity). As a rule, the constant values of the reaction rates are determined by such parameters.
Let us analyze an elementary example of closed cell population in which multiplication and death occur concurrently and which are abundant in nutrients. The questions arise: how is the number of cells changed in such a system with time, and can a stationary state eventually form in it when the number of cells remains the same? This kinetic problem may be solved with the use of differential equations. Let at moment t the concentration of cells in the environment be
N. The rate of the cell concentration changes in the environment
is the net sum of their multiplication rate (
vmitipl) and death rate (
vdeath).
In an ordinary case, the multiplication rate, which is the increase in the cell concentration per time unit, is proportional to their number at every moment, i.e.
where k1 is the proportionality constant dependent on the environmental conditions (temperature, the presence of nutrients, etc.)
Correspondingly
where k2 is the constant determining the intensity of processes of cell death. Hence it follows that
where k = k1−k2.
By solving the above equation we will see how the cell concentration is changed with time in the environment N = N(t). By integrating Eq. (1.1) we get
where N0 is the cell concentration at zero time t = 0 of the examining the system.
It can be seen that depending on the ratio of the death rate constant (k2) and multiplication rate constant (k1) the destiny of this closed population will be different. If k1 > k2, k > 0, the system will give rise to the unlimited growth of the cell number.
N(t) → ∞ at t → ∞.
If k1 < k2, the population will dye out with time
N(t) → ∞ at t → ∞.
And only in a particular case when k1 = k2 the number of cells will remain constant
N = N0.
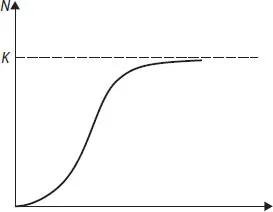
Another example of the model of the population growth in the environment with a limited amount of nutrients is the known equation of a logistic curve. The Verhulst equation is as follows
Here Nmax is the maximal population number possible under such conditions. Curve N = N(t) described by the above equation is shown in Fig. 1.1. At the initial period of growth, when N << Nmax the curve is exponential. Then, after the inflection, the slope gradually decreases and the curve approaches the upper asymptote N = Nmax, i.e. the maximal attainable level under such conditions.
But as compared to the typical chemical kinetics, the biological kinetics has the following specificity.
1. The variables can be not only substance concentrations but also other values.
2. The variables change not only in time but also in space (diffusion of reagents across biomembranes).
3. A biological system is heterogeneous in space and the conditions of the reagent interaction can vary in different sites of the system).
4. There exist special mechanisms of self-regulation functioning by the feedback principle.
5. The power of the polynomial in the righ...