
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Optimization of Logistics
About this book
This book aims to help engineers, Masters students and young researchers to understand and gain a general knowledge of logistic systems optimization problems and techniques, such as system design, layout, stock management, quality management, lot-sizing or scheduling. It summarizes the evaluation and optimization methods used to solve the most frequent problems. In particular, the authors also emphasize some recent and interesting scientific developments, as well as presenting some industrial applications and some solved instances from real-life cases.
Performance evaluation tools (Petri nets, the Markov process, discrete event simulation, etc.) and optimization techniques (branch-and-bound, dynamic programming, genetic algorithms, ant colony optimization, etc.) are presented first. Then, new optimization methods are presented to solve systems design problems, layout problems and buffer-sizing optimization. Forecasting methods, inventory optimization, packing problems, lot-sizing quality management and scheduling are presented with examples in the final chapters.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Modeling and Performance Evaluation
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Markovian processes
1.2.1. Overview of stochastic processes
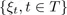
| T discrete | T continuous | |
|---|---|---|
| X discrete | Markov chains with a discrete state space | Markov processes with a discrete state space |
| X continuous | Markov chains w... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Dedication
- Title
- Copyright
- Chapter 1. Modeling and Performance Evaluation
- Chapter 2. Optimization
- Chapter 3. Design and Layout
- Chapter 4. Tactical Optimization
- Chapter 5. Scheduling
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app