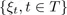![]()
Chapter 1
Modeling and Performance Evaluation
1.1. Introduction
A system, be it logistic or otherwise, may be considered as a set of interacting entities, capable of handling other entities that are internal or external to it. A model of a system is a logical, mathematical representation of its real behavior in a given context and following a given problem. A model is a decision-support tool that allows the study of a complex system through one or more simpler systems, replacing it in a scientific analysis, providing information about the studied system or, for example predicting the behavior of the initial system in various conditions.
We may distinguish between different types of model based on different characteristics. A model may be analogical (such as a scale model of a machine) or abstract (without physical representation). If time is not considered in the study, the model is static, and it is described as dynamic if the state of the system it represents evolves over time. If its evolution involves an element of chance, it is described as stochastic (as opposed to deterministic). The notions of deterministic and stochastic models are directly related to uncertainties. These uncertainties are, for example variations in operating times, variations in machine preparation time, etc. If the model requires a formal equation, it is described as mathematical, and it will be called numerical if it is based on a simulation.
The aim of modeling is therefore to best reproduce the actual operation of the studied system. Hence, the physical and technical characteristics of the system must be taken into consideration. This information constitutes a model’s input data, and allows the determination, in the most precise possible manner, of output data known as the performance indicators of the system.
In this Chapter, we present a non-exhaustive list of methods and tools for modeling and evaluating the performance of logistics systems, such as Markov chains, Petri nets, the Gershwin decomposition method and discrete-event simulation.
1.2. Markovian processes
Probability theory is a mathematical science that began in the 17th Century with the work of Galileo on physical measurement errors. It was only later in the 19th Century that A. Markov (1856–1922) defined the basis of the theory of stochastic processes, creating the model that carries his name. Markov chains occupy an important place among stochastic models and are currently used in numerous applications (economic, meteorological, military, computational, etc.). Their use in production systems is significant (queuing networks, maintenance policy, fault detection, etc.). A Markov model is well adapted to the study and analysis of production systems because it provides a simple graphical representation while retaining its powerful analytical properties.
1.2.1. Overview of stochastic processes
Numerous authors have introduced stochastic processes in their works. We cite the work of [FEL 68].
DEFINITION 1.1.– A stochastic process is a family of random variables ξt:
where the parameter t explores the set T . T may belong to the set of natural numbers, real numbers, etc.
If T is discrete and countable: {ξt} form a stochastic sequence.
If T is a finite or infinite interval: {ξt} form a continuous process.
Note that T typically represents an interval of time.
Let X be the state space. X is the set whence the variables ξt take their values. X may be discrete or continuous.
From the definition of random processes [1.1], we distinguish between four Markov processes according to the discrete or continuous nature of the state space and of the set T (see Table 1.1).
Table 1.1. The different Markov processes
| T discrete | T continuous |
| X discrete | Markov chains with a discrete state space | Markov processes with a discrete state space |
| X continuous | Markov chains w... |