
The Sponsorship Handbook
Essential Tools, Tips and Techniques for Sponsors and Sponsorship Seekers
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
The Sponsorship Handbook
Essential Tools, Tips and Techniques for Sponsors and Sponsorship Seekers
About this book
Using the tools, techniques, advice and best practice advocated in this book both sponsors and sponsor seekers will benefit from better servicing and activation once a sponsorship is implemented, with metrics that enable data-based accountability rather than hearsay.
"Everyone in the sponsorship industry, from the biggest events and properties to the smallest, are benefitting from the increasing knowledge, data availability, metrics and professionalism in using sponsorship. The Sponsorship Handbook is a part of that process which we hope will bring future success and proven sound results to all in the complex and exciting world of sponsorship."
—Luis Vicente, Head of Partnerships, Manchester City Football Club
"An indispensable reference for any marketer who is keen to build his/her brand using sponsorship; the new ascending way to empower brands."
—Faisal Al-Dail, Saudi Post
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information

- What sponsorship is, and is not, in the context of modern sponsorship practice.
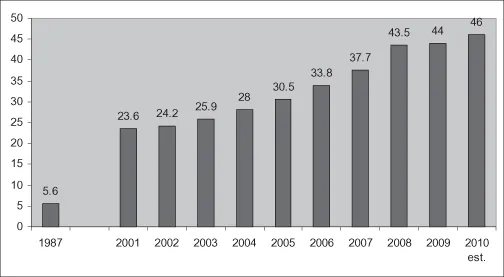
- The size of the industry, and why it continues to see growth at a time when advertising spend is slowing.
- The key players and the range of sponsorship opportunities, target audiences and possible sponsorship objectives that should be taken into consideration.
- Tangible and intangible sponsorship assets and how some of these might be valued.
- The process of sponsorship from both a sponsor’s and a rights-holder’s perspective.
- A discussion about when to use internal headcount versus external support to deliver on sponsorship objectives.

- Commercial: Modern sponsorship of the sort undertaken by businesses large and small is targeted at delivering some sort of commercial outcome for business owners, whether the company is publicly or privately owned. The benefits may be accrued in terms of additional revenues or cost savings in the profit and loss account, or as an increase in the value of brand equity on the balance sheet. While an individual undertaking a challenge to raise money for good causes – such as running a marathon or learning a new skill – is a laudable activity, it is outside the scope of this definition, and therefore this book.
- Mutual: There is progressive acceptance that the benefits of a sponsorship relationship should represent a win–win partnership for both the sponsor’s organization and that of the sponsored activity.
- Contract: This may be written out in detail or be based on an oral agreement, but the fundamentals of contract law, as applied in the appropriate judicial system, will apply to the relationship. The rights-holder is offering for sale the right of association and possibly other benefits, which are accepted by the sponsor and confirmed by the provision of some form of consideration, which may be cash or defined value in kind. An informal agreement of mutual association with no consideration does not constitute sponsorship under the ICC definition.
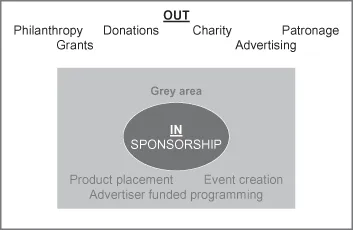
- Cause-related marketing – Red, the global AIDS-related fundraising initiative, is a good example where a variety of brands have come together to raise money to fight AIDS while benefiting from enhanced brand equity.
- Product placement – Whether it is BMW in the Bond movies or Coca-Cola being prominently consumed by X Factor USA judges, consumers are progressively aware that brands are capitalizing on collective aspirations to market their products.
- Advertiser-funded programming – Gillette’s World of Sport is the classic example of the genre, associating shaving products with performance.
- Event creation – The Red Bull Air Race or Nike 10k Runs look like sponsored events but are both in fact owned by the relevant brand, representing a desire by them to have more control of the activity than would normally be available in a true sponsorship relationship.
- Economic development is currently focusing attention on sponsorship as a marketing tool because of the aspirations that greater economic freedom brings to individuals. In agrarian society wealth is highly concentrated with the majority existing at or below subsistence level with nothing to spare for discretionary activity. Economic development creates both the time and the cash for individuals to spend on discretionary items, usually initially allocated to physical comfort. As prosperity becomes the norm, so more money is available to allocate, first, to burden-reducing services, and then to leisure pursuits. Fully mature markets have now moved into an experience economy where people are looking for self-actualizing experiences. This is a need to which brands are responding, whether it is the “terrific experience” of dining at Pizza Hut, shopping at Apple or applying a grooming product. The challenge for many brands is to make these experiences real for customers. Sponsorship facilitates the bringing alive of brand experiences.
- Social evolution is the second trend driving growth in the sponsorship industry. Historically people identified themselves by the feudal lord they served. More recently, identity was linked to the company that provided your employment. Similarly, women started to gain their own identity, no longer recognized as merely their father’s daughter or husband’s wife. The outcomes of these societal changes are that people are looking for new badges of allegiance. These may be found in politics, sport, religion or other pursuits which bind groups together in real or virtual communities at the consumer level.
This social evolution has also impacted how corporations see their role in society. The introduction of triple bottom line accounting has meant that companies can no longer focus merely on economic success in terms of profit and dividends. Now they also have to consider their social and environmental impact. This has led companies to invest at grass roots levels in education, health, sport and culture, aiming not only to make a contribution at the local community level but also to have a global impact.
- However, the technological revolution represe...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Dedication
- FOREWORD
- PREFACE
- ABOUT THE AUTHORS
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- HOW TO USE THIS BOOK
- CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO SPONSORSHIP
- Part I: Sponsors
- Part II: Sponsorship Seekers
- Part III: The Way Ahead
- GLOSSARY
- Index