![]()
1 Introduction
1.1 Presentation of Problem and Objectives
In the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, the area of sports has become a significant economic factor worldwide. Due to the increasing commercialisation of sports, business management know-how is becoming ever more essential in this field. The economics of sports is a relatively new discipline, but one that has undergone very fast-paced development in recent years. Not the least of the reasons why sports economics and sports management are exciting research fields is that this is where diverse approaches to an appropriate method mix in terms of substance and problem come together. Some even speak of a new scientific “subdiscipline” (Albach and Frick 2002: vii) or more so of an independent “branch of science” (Heinemann 2001: 17). Within sports management, the discipline with the strongest differentiation to date is that of sports marketing, i.e. professionalism in terms of business management is the most advanced in the area of sports marketing.
“Consumers love events, corporations love consumers … this is a match made in heaven” (D’Alessandro 1993: 507). In consideration of this “magic formula”, it is especially companies that operate internationally who are in search of attractive sports events that have a great deal of appeal to a broader public. Therefore, it is not surprising that it is primarily international sports events that are utilised by numerous companies to embed their target group-oriented communications in an attractive environment. There are many good reasons why marketing with sports events is of such great interest to companies. The aim is to create a positive image transfer from the sports event to the brand or the company. The message is communicated in the context of an attractive sporting environment. High (international) reach and thereby comparatively low cost per mille prices can thus be achieved. The multiplier effect of mass media can be fully utilised.
The increasing intensity of competition in the sponsorship market has resulted in a price explosion for sponsorships, with the ensuing consequence that not all companies interested in an event are able to afford or willing to commit to an official sponsorship. Additionally, the design of the sponsorship rules and regulations for mega events (e.g. the guarantee of industry exclusivity for official sponsors) frequently deprives competitors of any opportunity for “legitimate” contact with their target groups in the context of the event. Ambush marketing is the practice by companies of using their own marketing to create an impression of an association with the event to the event audience, although the companies in question have no legal (or only underprivileged or non-exclusive) marketing rights for this event sponsored by third parties.
The line between violation of sponsorship rights and creative–innovative communications policy is often a very fine one, which is why ambush marketing is a fundamentally controversial topic of discussion. The growing aggressiveness in the communications and sports markets has resulted in the appearance of ambush marketing worldwide and its continually increasing pervasiveness.
The aim of this book is to make a contribution to the in-depth scientific examination of the phenomenon of ambush marketing. The objectives of this study are as follows:
- Description: survey and assessment of the entire problem area of ambush marketing (descriptive scientific objective).
- Explanation: identification and review of the relevant structures, processes, influencing factors and interactions (theoretical scientific objective).
- Design: generation of solutions or deduction of action recommendations (pragmatic scientific objective).
1.2 Structure of the Approach and Course of the Study
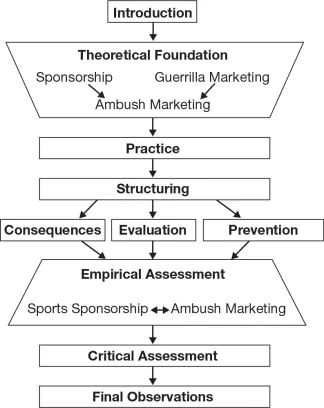
Chapter 2 of this study addresses the theoretical foundation of ambush marketing. Based on the essential principles of sponsorship, ambush marketing is categorised within the overarching concept of guerrilla marketing and characterised as a guerrilla alternative to sports event sponsorship.
In Chapter 3 selected cases of ambush marketing in actual practice that generated a great deal of buzz and media presence are presented and subjected to critical assessment.
The point of departure for structuring the diverse strategies and manifestations of ambush marketing in Chapter 4 is established by the presentation and critical assessment of existing systematisation approaches in literature. Based on this, the author develops his own integrated structuring model for ambush marketing, which encompasses ambush marketing categories differentiated from one another that, on subsequent levels, are further broken down into differentiated case groups per category and differentiated cases per case group. The cases of ambush marketing observed in the context of the 2010 FIFA Football World Cup in South Africa are integrated into the structuring model and implications deduced from these.
Based on this, in Chapter 5 the consequences for the participating stakeholders that result from ambush marketing are elaborated and developed.
Subsequently, Chapter 6 follows up with an interdisciplinary evaluation of ambush marketing in terms of both legal–statutory and ethical–moral perspectives.
In Chapter 7 the challenges for organisers and official sponsors of sports events in the prevention of ambush marketing are extrapolated.
Chapter 8 is dedicated to the empirical research of the effects of ambush marketing. Initially, an overview of the current status of effectiveness research on ambush marketing is presented. It is followed by the empirical study of the author on ambush marketing in the context of the 2006 Football World Cup in Germany. A total of over 2,000 teenagers aged 13 to 18 were interviewed. The focus of the analysis is on image values and recall performance of the interviewees with regard to companies who used the World Cup platform as part of their communications policy. Based on this, the causes for confusion of ambush marketers with official sponsors are analysed in order to determine the impact of ambush marketing.
In the critical assessment of ambush marketing in Chapter 9 both the pro and contra positions on ambush marketing are examined before a conclusive evaluation of the phenomenon is conducted. Implications for the actual practice of sports marketing are deduced from the results of these observations.
The essential insights of this study are summarised in the context of final observations in Chapter 10. Furthermore, a short perspective for the future of ambush marketing is provided.
Figure 1.1 provides an overview of the structure of this study in graphic form.
Figure 1.1 Structure of the approach and course of the study
![]()
2 Theoretical Foundation of Ambush Marketing
For many companies, it is major international sporting events in particular, for example the Olympics or the Football World Cup and European Championships that constitute the ideal platform for the integration of their target group-specific communications into an attractive sports environment. Sports event organisers therefore sell exclusive marketing rights for their events to sponsors. In return, official sponsors acquire exclusive options to utilise the event for their own advertising purposes. Ambush marketing, on the other hand, is the method used by companies that do not actually hold legal marketing rights to an event, but still use their marketing communications activities to create the impression of an association with this event to their audience.
While sports sponsorship has already established itself in theory and practice, ambush marketing is a relatively new, innovative method to make use of sports events in terms of communications. Both of these alternative communications options shall be presented and critically assessed in the following. As sponsorship is the original soil and breeding ground for ambush marketing, its fundamental precepts will be looked at first.
2.1 Sponsorship as the Basis of Ambush Marketing
Sponsorship is classified among the non-classical forms of marketing communications policy and addresses people in non-commercial situations. It is precisely through sponsorship that those target groups can be reached who are, for example, negatively disposed to advertising or cannot be reached via classical communication tools. Also, a sponsorship commitment generally tends to be accepted more so than classical advertising, since sponsorship per se is based on a certain degree of promotional intent (Nufer and Bühler 2011c).
2.1.1 Fundamentals of Sponsorship
Today, sponsorship is a well-established facet in the marketing plans of companies as well as in professional literature on corporate communications. Sponsorship has gained this level of acceptance relatively quickly, for even in the mid 1980s this communications tool was neither widely used nor theoretically well developed (Drees 2003).
2.1.1.1 Definition and Attributes of Sponsorship
One of the most frequently cited definitions of sponsorship is attributed to Bruhn (2010: 6f.). He defines and structures sponsorship generally as the:
- Analysis, planning, execution and control of all activities
- that with the provision of money, materials, services or knowhow by companies and institutions
- for the promotion of persons and/or organisations in the areas of sports, culture, social issues, environment and/or the media
- are associated under contractual regulation of the services of the sponsor and the return services of the sponsored party
- to thereby, at the same time, achieve marketing and corporate communications objectives.
One refers to a sponsorship when the sponsor and the sponsored party have agreed to jointly conduct or execute a specific project in a predetermined time-frame under specific conditions (Bruhn 2005).
Bruhn (2010) distinguishes six constitutive features of sponsorship that, irrespective of differing approaches, are common to all sponsorship activities:
- Sponsorship is based on the principle of performance and consideration: the sponsors provide their funding in the expectation of the receipt of specific return performance or service from the sponsored parties. The sponsored parties, in turn, also seek to benefit from more than just the financial support of the sponsor in this barter transaction by realising an image enhancement and using the sponsorship to expand their networks.
- In sponsorship the promotional aspect in terms of the sponsored party is given expression: sponsorship is not the pure sale of advertising space for payment, but rather the identification of sponsors with the inherent substance of their functions.
- Sponsorship fulfils communicative functions: these are provided by the sponsored party, transmitted by media or may also be created by the sponsors themselves.
- Sponsorship demands a systematic planning and decision-making process: based on a situation analysis and the formulation of objectives, measures must be planned, executed and monitored individually.
- An image transfer constitutes an essential objective of sponsorship. For image building, sponsorship does not allow for the separation of the message from the medium. The object of a sponsorship commitment (e.g. a sports event) embodies the message as well as the medium per se.
- From a company’s perspective, sponsorship is a building block of integrated communications: it cannot be an isolated measure, but...