
- 840 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book will enable electrical engineers and technicians in the fields of the biomedical, computer, and electronics engineering, to master the essential fundamentals of DSP principles and practice. Coverage includes DSP principles, applications, and hardware issues with an emphasis on applications. Many instructive worked examples are used to illustrate the material and the use of mathematics is minimized for easier grasp of concepts.In addition to introducing commercial DSP hardware and software, and industry standards that apply to DSP concepts and algorithms, topics covered include adaptive filtering with noise reduction and echo cancellations; speech compression; signal sampling, digital filter realizations; filter design; multimedia applications; over-sampling, etc. More advanced topics are also covered, such as adaptive filters, speech compression such as PCM, u-law, ADPCM, and multi-rate DSP and over-sampling ADC.- Covers DSP principles and hardware issues with emphasis on applications and many worked examples- End of chapter problems are helpful in ensuring retention and understanding of what was just read
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
Objectives
1.1 Basic Concepts of Digital Signal Processing
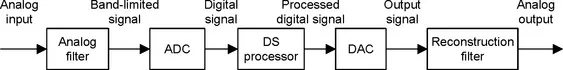
1.2 Basic Digital Signal Processing Examples in Block Diagrams
1.2.1 Digital Filtering

Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- About the Author
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
- Chapter 2: Signal Sampling and Quantization
- Chapter 3: Digital Signals and Systems
- Chapter 4: Discrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum
- Chapter 5: The z-Transform
- Chapter 6: Digital Signal Processing Systems, Basic Filtering Types, and Digital Filter Realizations
- Chapter 7: Finite Impulse Response Filter Design
- Chapter 8: Infinite Impulse Response Filter Design
- Chapter 9: Hardware and Software for Digital Signal Processors
- Chapter 10: Adaptive Filters and Applications
- Chapter 11: Waveform Quantization and Compression
- Chapter 12: Multirate Digital Signal Processing, Oversampling of Analog-to-Digital Conversion, and Undersampling of Bandpass Signals
- Chapter 13: Image Processing Basics
- A: Introduction to the MATLAB Environment
- B: Review of Analog Signal Processing Basics
- C: Normalized Butterworth and Chebyshev Functions
- D: Sinusoidal Steady-State Response of Digital Filters
- E: Finite Impulse Response Filter Design Equations by the Frequency Sampling Design Method
- F: Some Useful Mathematical Formulas
- Bibliography
- Answers to Selected Problems
- Index