
- 172 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Food Processing and Preservation
About this book
This book provides an exhaustive coverage on all the types of food products-fruits, vegetables, cereals, dairy and meat processing and their preservation. It also provides a brief introduction to their importance in employment generation.
Note: T&F does not sell or distribute the hardback in India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER-1
INTRODUCTION TO PRESERVATION OF FOODS
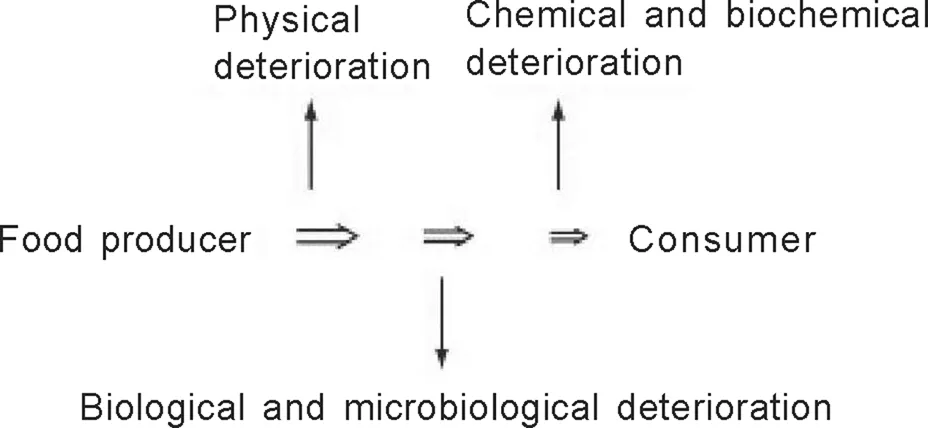
Food preservation consists of the application of science-based knowledge through a variety of available technologies and procedures, to prevent deterioration and spoilage of food products and extend their shelf-life, while assuring consumers a product free of pathogenic microorganisms. Shelf-life may be defined as the time it takes a product to decline to an unacceptable level. Deterioration of foods will result in loss of quality attributes, including flavor, texture, color, and other sensory properties. Nutritional quality is also affected during food deterioration. Physical, biological, microbiological, chemical, and biochemical factors may cause food deterioration. Preservation methods should be applied as early as possible in the food production pipeline and therefore, include appropriate postharvest handling before processing of both plant and animal foods (Figure 1).
Processing techniques usually rely on appropriate packaging methods and materials to assure continuity of preservation. Handling of processed foods during storage, transportation, retail, and by the consumer also influences the preservation of processed foods.
All of the processes used for preserving food at home are based on the principle of preservation.
CHAPTER-2
ROLE OF FOOD PROCESSING/PRESERVATION IN INCOME AND EMPLOYMENT GENERATION
INTRODUCTION
The diversification and modernization of the present agricultural and other related activities supported by efficient on and off farm processing of the commodities for the purpose of value-addition is expected to increase food production and create employment and income generation. Adding value to food commodities after harvest is also aimed at minimizing the losses during storage and to maintain the quality of product. Efficient post-production practices, particularly the preservation and processing of agricultural and allied produces may bring a wide range of benefits to the people in this country, generating job opportunities by opening up village-level processing units. The goals of post-harvest and food processing technology are loss prevention as well as adding value to the harvested biomass, which result in more income to the farmers/processors and better quality produce provided to the consumers. Post-harvest and food processing technology are commodity-and location-specific and it is done at home, village and/or cottage levels at small and large industrial scale. On-farm post-harvest storage and primary processing integrated with production technology help to generate more employment opportunities and additional income for rural people. Minimization of the post-harvest losses is an important means to increase per capita food availability. It also helps to generate more employment and income. Investment in post-harvest measures is more economical and time saving than in productivity to obtain the same amount of a particular commodity. Furthermore, post-harvest measures automatically add value to the raw commodities as they pass on their marketing channels. Adoption of post-harvest technologies and value additive measures are very strong tools for rural and social development through employment and income generation. Development and adoption of efficient value addition practices will enhance national food supply and sustain food security even at the household level. Fruits and vegetables processing industries have a good deal of potential in serving the rural economy. First, it helps in generating more employment for rural people. It will also check mobility of rural masses towards urban areas in search of employment. Employment opportunities offered by agro-processing industries are plenty to the farm population and entrepreneur seeking self-employment. Cottage scale units particularly offer self-employment opportunities. Traditionally women handle food and are familiar with skills of food processing. In order to improve the status of living of woman and rural food processing, low cost appropriate fruit and vegetable processing technologies offer excellent opportunities for production of processed foods. The improvement of status of socially backward and landless labor classes will be possible only through providing non-farm employment at their doorsteps. This will generate a sense of security and confidence amongst rural people for overcoming uncertainty in agricultural income and providing self-employment to the land-less labor. The locally available untapped resources should be used effectively.
Food processing as a scientific and technological activity covers a broader area than food preparation and cooking. It involves the application of scientific principles to slow down the natural processes of fruit decay caused by microorganisms, enzymes in the food or environmental factors such as, heat, moisture and sunlight- and so, preserve the food. In developing countries like India, food processing is a method of generating employment and family incomes but producers have to compete with others in the same country and with imported products where in packaging and preservation play a great role. Processing of foods involves methods of business planning, work organization and quality assurance that are likely to be unfamiliar to traditional preservers but which are essential to ensure successful and profitable production.
Issues to be considered when addressing different objectives of food processing
- Issues that affect food security and nutritional improvement programmes
- Nutrition education
- Health and hygiene training
- Improved communication
- Confidence building measures
- Credit support systems
- Improvements to equipments and tools
- Improved infrastructure and transport
- Seed banks and other sources of agricultural inputs.
- Issues that affect enterprise development programmes
- Suppliers of specialist equipment Market awareness and consumer preferences.
- Marketing strategies, promotion and packaging.
- Methods of financial control.
- Developing trust with suppliers and retailers.
- – Quality assurance.
- – Hygiene and sanitation for production
- – Food legislation.
- – Taxation and business legislation.
- – Training in management and business planning.
- – Finance and credit suppliers.
- – Staff training in production technologies.
- – Ingredients.
Status and Scope of Food Business in India
The growth rate of food production being faster than population growth has led to development in agro industry particularly Food Industry in India through the successive five year plans. Processed foods have slowly won the hearts of consumers in the recent years and the production is increasing but still not sufficient to meet the demands of people. The food industry has to dedicate itself from raw material selection, mode of preparation, process to be adopted, packaging system to be used, the quality control of raw material, final product as well whole operations involved to meet the local and international standards.
Evolution of Food Processing Industry
The food processing industry in India has evolved from different phases, basic development phase-1947 to 1970, transformation phase from 1970-1990, early growth phase of 1999- 2002 and consolidation phase 2003 and beyond as influenced by economic growth, changing consumer attitudes and government policies. The potential for this industry in India is enormous provided there is good infrastructure, better cultivation practices, systematic processing approach with the backing of resources and policies. Today, India is the world’s leading producer of foods starting from sugar, tea, milk to fruits and vegetables. India produces 601 million tons of food as against 608 million tonnes in US. The food industry structure reveals that only 55% of food production is contributed by small scale and organized sectors while 42% is being produced by the unorganized sector. Indian Food Industry is fifth largest, employs 19% work force, 14% industrial output, 5.5% GDP. The present worth of food business in India is Rs. 8,70,000 crores. The composition of Indian food industry reveals that major industry consists of oils and fats (36%), followed by dairy products (16.9%), cold beverages (15.6%) and bever...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- 1. Introduction To Preservation of Foods
- 2. Role of Food Processing/Preservation in Income and Employment Generation
- 3. Processing and Preservation of Fruits and Their Products
- 4. Processing and Preservation of Vegetables and Their Products
- 5. Processing and Preservation of Cereal and Cereal Products
- 6. Processing and Preservation of Dairy and Dairy Based Products
- 7. Processing and Preservation of Meat and Meat Products
- References
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Food Processing and Preservation by H.R. Naik,Tawheed Amin in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Food Science. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.