
- 344 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This is the first book that focuses on practical algorithms for polynomial inequality proving and discovering. It is a summary of the work by the authors and their collaborators on automated inequality proving and discovering in recent years. Besides brief introduction to some classical results and related work in corresponding chapters, the book mainly focuses on the algorithms initiated by the authors and their collaborators, such as real root counting, real root classification, improved CAD projection, dimension-decreasing algorithm, difference substitution, and so on. All the algorithms were rigorously proved and the implementations are demonstrated by lots of examples in various backgrounds such as algebra, geometry, biological science, and computer science.
Contents:
- Preface
- Basics of Elimination Method
- Zero Decomposition of Polynomial System
- Triangularization of Semi-Algebraic System
- Real Root Counting
- Real Root Isolation
- Real Root Classification
- Open Weak CAD
- Dimension-Decreasing Algorithm
- SOS Decomposition
- Successive Difference Substitution
- Proving Inequalities Beyond the Tarski Model
Readership: Researchers and graduate students in computational real algebraic geometry, optimization and artificial intelligence.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Basics of Elimination Method
1.1Pseudo-division
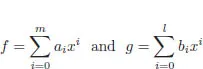
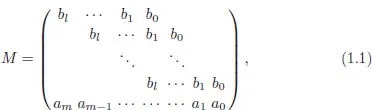
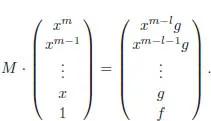
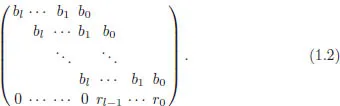
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- 1. Basics of Elimination Method
- 2. Zero Decomposition of Polynomial System
- 3. Triangularization of Semi-Algebraic System
- 4. Real Root Counting
- 5. Real Root Isolation
- 6. Real Root Classification
- 7. Open Weak CAD
- 8. Dimension-Decreasing Algorithm
- 9. SOS Decomposition
- 10. Successive Difference Substitution
- 11. Proving Inequalities Beyond the Tarski Model
- Bibliography
- Index