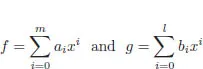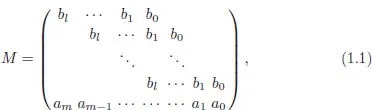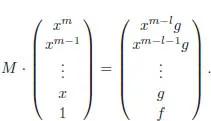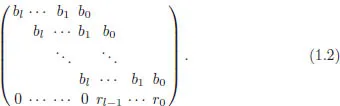Automated Inequality Proving And Discovering
Bican Xia, Lu Yang
- 344 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Automated Inequality Proving And Discovering
Bican Xia, Lu Yang
Über dieses Buch
This is the first book that focuses on practical algorithms for polynomial inequality proving and discovering. It is a summary of the work by the authors and their collaborators on automated inequality proving and discovering in recent years. Besides brief introduction to some classical results and related work in corresponding chapters, the book mainly focuses on the algorithms initiated by the authors and their collaborators, such as real root counting, real root classification, improved CAD projection, dimension-decreasing algorithm, difference substitution, and so on. All the algorithms were rigorously proved and the implementations are demonstrated by lots of examples in various backgrounds such as algebra, geometry, biological science, and computer science.
Contents:
- Preface
- Basics of Elimination Method
- Zero Decomposition of Polynomial System
- Triangularization of Semi-Algebraic System
- Real Root Counting
- Real Root Isolation
- Real Root Classification
- Open Weak CAD
- Dimension-Decreasing Algorithm
- SOS Decomposition
- Successive Difference Substitution
- Proving Inequalities Beyond the Tarski Model
Readership: Researchers and graduate students in computational real algebraic geometry, optimization and artificial intelligence.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
Chapter 1
Basics of Elimination Method
1.1Pseudo-division