
Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials, Physico-Chemical and Mechanical Characterization
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials, Physico-Chemical and Mechanical Characterization
About this book
The Handbook of Composites From Renewable Materials comprises a set of 8 individual volumes that brings an interdisciplinary perspective to accomplish a more detailed understanding of the interplay between the synthesis, structure, characterization, processing, applications and performance of these advanced materials. The handbook covers a multitude of natural polymers/ reinforcement/ fillers and biodegradable materials. Together, the 8 volumes total at least 5000 pages and offers a unique publication.
This 3rd volume of the Handbook is solely focused on the Physico-Chemical and Mechanical Characterization of renewable materials. Some of the important topics include but not limited to: structural and biodegradation characterization of supramolecular PCL/HAP nano-composites; different characterization of solid bio-fillers based agricultural waste material; poly (ethylene-terephthalate) reinforced with hemp fibers; poly (lactic acid) thermoplastic composites from renewable materials; chitosan –based composite materials: fabrication and characterization; the use of flax fiber reinforced polymer (FFRP) composites in the externally reinforced structures for seismic retrofitting monitored by transient thermography and optical techniques; recycling and reuse of fiber reinforced polymer wastes in concrete composite materials; analysis of damage in hybrid composites subjected to ballistic impacts; biofiber reinforced acrylated epoxidized soybean oil (AESO) biocomposites; biopolyamides and high performance natural fiber-reinforced biocomposites; impact of recycling on the mechanical and thermo-mechanical properties of wood fiber based HDPE and PLA composites; lignocellulosic fibers composites: an overview; biodiesel derived raw glycerol to value added products; thermo-mechanical characterization of sustainable structural composites; novel pH sensitive composite hydrogel based on functionalized starch/clay for the controlled release of amoxicillin; preparation and characterization of biobased thermoset polymers from renewable resources; influence of natural fillers size and shape into mechanical and barrier properties of biocomposites; composite of biodegradable polymer blends of PCL/PLLA and coconut fiber - the effects of ionizing radiation; packaging composite materials from renewable resources; physicochemical properties of ash based geopolymer concrete; a biopolymer derived from castor oil polyurethane; natural polymer based biomaterials; physical and mechanical properties of polymer membranes from renewable resources
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Structural and Biodegradation Characterization of Supramolecular PCL/HAp Nanocomposites for Application in Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Hydroxyapatite: A Bioceramic of Renewable Resource
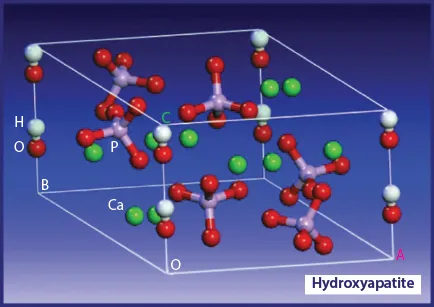
1.2 Biomedical Applications of HAp
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Dedication
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Structural and Biodegradation Characterization of Supramolecular PCL/HAp Nanocomposites for Application in Tissue Engineering
- Chapter 2: Different Characterization of Solid Biofillers-Based Agricultural Waste Materials
- Chapter 3: Poly (ethylene-terephthalate) Reinforced with Hemp Fibers: Elaboration, Characterization, and Potential Applications
- Chapter 4: Poly(Lactic Acid) Thermoplastic Composites from Renewable Materials
- Chapter 5: Chitosan-Based Composite Materials: Fabrication and Characterization
- Chapter 6: The Use of Flax Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FFRP) Composites in the Externally Reinforced Structures for Seismic Retrofitting Monitored by Transient Thermography and Optical Techniques
- Chapter 7: Recycling and Reuse of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Wastes in Concrete Composite Materials
- Chapter 8: Analysis of Damage in Hybrid Composites Subjected to Ballistic Impacts: An Integrated Non-Destructive Approach
- Chapter 9: Biofiber-Reinforced Acrylated Epoxidized Soybean Oil (AESO) Biocomposites
- Chapter 10: Biopolyamides and High-Performance Natural Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites
- Chapter 11: Impact of Recycling on the Mechanical and Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Wood Fiber Based HDPE and PLA Composites
- Chapter 12: Lignocellulosic Fibers Composites: An Overview
- Chapter 13: Biodiesel-Derived Raw Glycerol to Value-Added Products: Catalytic Conversion Approach
- Chapter 14: Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of Sustainable Structural Composites
- Chapter 15: Novel pH Sensitive Composite Hydrogel Based on Functionalized Starch/clay for the Controlled Release of Amoxicillin
- Chapter 16: Preparation and Characterization of Biobased Thermoset Polymers from Renewable Resources and Their Use in Composites
- Chapter 17: Influence of Natural Fillers Size and Shape into Mechanical and Barrier Properties of Biocomposites
- Chapter 18: Composite of Biodegradable Polymer Blends of PCL/PLLA and Coconut Fiber: The Effects of Ionizing Radiation
- Chapter 19: Packaging Composite Materials from Renewable Resources
- Chapter 20: Physicochemical Properties of Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete
- Chapter 21: A Biopolymer Derived from Castor Oil Polyurethane: Experimental and Numerical Analyses
- Chapter 22: Natural Polymer-Based Biomaterials and its Properties
- Chapter 23: Physical and Mechanical Properties of Polymer Membranes from Renewable Resources
- Index
- End User License Agreement