
Geriatric Emergencies
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Geriatric Emergencies
About this book
Geriatric Emergencies is a practical guide to the common conditions affecting older patients who present in an emergency to hospital or primary care.
Beginning with the essentials of history taking and clinical examination, the book covers a comprehensive range of emergencies, emphasizing the different management approaches which may be required in older patients. Common geriatric presentations such as falls, delirium and stroke, are explored in detail in addition to more diverse topics such as abdominal pain, major trauma and head injury. Ethical considerations such as advanced care planning, palliative care and capacity assessment are discussed with practical tips on communicating with patients and their relatives.
Geriatric Emergencies provides concise up-to-date guidance to the emergency management of the older patient. It is a recommended resource for all health professionals working in the acute environment, in which a large proportion of patients are aged over 65.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction to geriatric emergency medicine
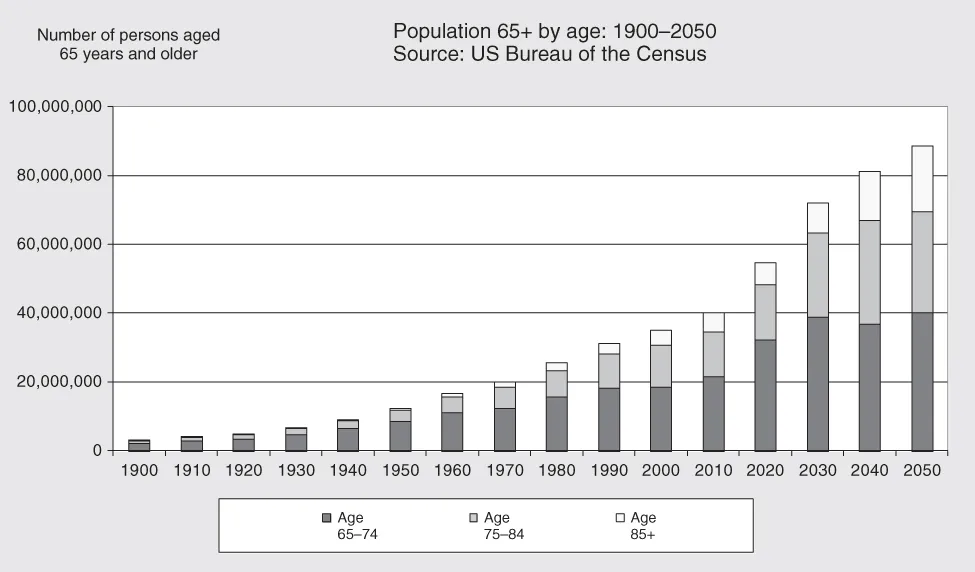
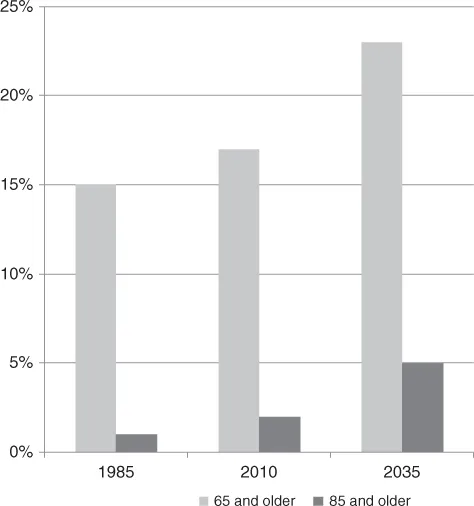
Demographics
KEY POINT
Emergency presentations
KEY POINT
Frailty at the front door
Box 1.1 The frailty phenotype (8)
- Unintentional weight loss (10 lbs over past year)
- Self-reported exhaustion
- Weakness (reduced grip strength)
- Slow walking speed
- Low physical activity
- No criteria = Robust
- 1–2 criteria = Pre-frail
- 3 or more criteria = Frail.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- List of Abbreviations
- Chapter 1: Introduction to geriatric emergency medicine
- Chapter 2: Essentials of assessment and management in geriatric emergency medicine
- Chapter 3: Special skills in geriatric emergency medicine
- Chapter 4: Vulnerable adults and elder abuse
- Chapter 5: Chest pain and atrial fibrillation
- Chapter 6: Dyspnoea
- Chapter 7: Infection and sepsis
- Chapter 8: Falls and immobility
- Chapter 9: Syncope
- Chapter 10: Dizziness
- Chapter 11: Major trauma
- Chapter 12: Fractures and back pain
- Chapter 13: Skin trauma
- Chapter 14: Head injury
- Chapter 15: Abdominal emergencies
- Chapter 16: Diabetic and environmental emergencies
- Chapter 17: Acute kidney injury and metabolic emergencies
- Chapter 18: Delirium
- Chapter 19: Stroke and transient ischaemic attack
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app