
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fogoros' Electrophysiologic Testing
About this book
The classic guide to applying, performing and interpreting EP tests, updated for the latest trends and developments in the field
For more than thirty years, Electrophysiologic Testing has been a trusted introduction to the field of electrophysiology for anyone needing to quickly acquaint themselves with basic concepts and procedures of EP testing, especially medical students, residents, nurses and technicians. At the same time, it also has served as a ready reference for medical practitioners wanting to brush up on aspects of electrophysiology, or to fine-tune their mastery of the field.
Updates and additions featured in the Sixth Edition of this classic guide include extensive new material on the ablation of cardiac arrhythmias, including new chapters on the ablation of atrial fibrillation, typical and atypical atrial flutters and ventricular arrhythmias.
The ultimate guide to applying, performing and interpreting EP tests to optimise the treatment of patients with cardiac arrhythmias, Electrophysiologic Testing, Sixth Edition:
- Clarifies the role of electrophysiology in the evaluation of cardia arrhythmias
- Provides clear summaries of complex topics
- Features a uniquely user-friendly style that makes information easy to digest and recall
- Offers clear, step-by-step guidance on performing EP tests and interpreting their results
- Reviews the latest developments in therapeutic electrophysiology
As with all previous editions, this updated and revised Sixth Editi on was written with the goal of demystifying electrophysiology, and making it readily accessible to virtually anyone with a professional need. To that end, Drs. Fogoros and Mandrola have once again turned in a masterful performance.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles
1
The Cardiac Electrical System
The anatomy of the heart’s electrical system
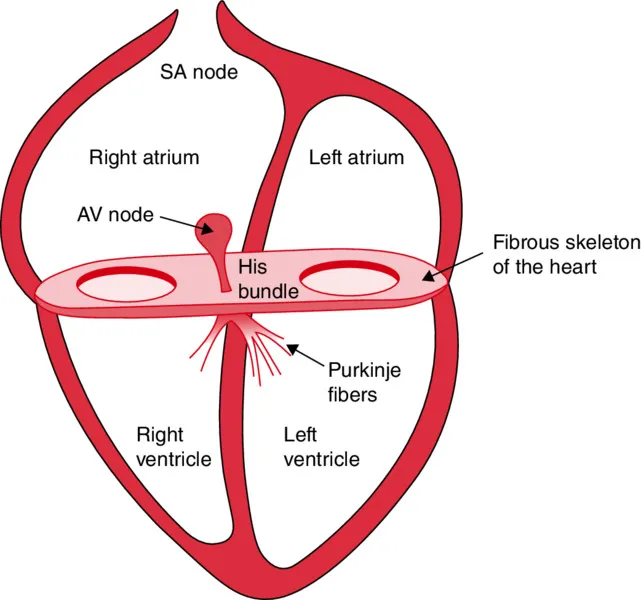
The cardiac action potential
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface to the Sixth Edition
- Part I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles
- Part II The Electrophysiology Study in the Evaluation and Therapy of Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Questions and Answers
- Index
- EULA
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app