
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Essential Clinical Oral Biology
About this book
Essential Clinical Oral Biology is an accessible guide to oral biology, introducing the scientific knowledge necessary to succeed in clinical practice.
- Student-friendly layout with clinical photographs throughout
- Each chapter has clearly defined key topics and learning objectives
- Covers the essentials: what you need to know and why
- Companion website featuring interactive MCQs, teaching presentations and downloadable images
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Essential Clinical Oral Biology by Stephen Creanor in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Oral Health & Surgery. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
An Introduction to the Human Dentition
Stephen Creanor
Key Topics
- Overview
- Descriptive terms applied to the human dentition
- Tooth nomenclature and the FDI tooth index
Learning Objectives
- To be familiar with the terms describing the various aspects of the dentition
- To be aware of the indices used in the charting of teeth and in particular the FDI tooth index
Overview
This chapter will introduce you to a series of terms which are applied to the various surfaces of the human dentition. Such terms are used constantly within the clinical scenario to describe the exact location of dental disease and the extent of dental restorations and so on. You must become familiar with these terms – you will be expected to know them in clinic. You should be familiar with the major characteristics of each tooth type, to enable you to identify the following:
- Is the tooth permanent (secondary) or primary (deciduous)?
- Has the tooth come from the upper or lower arch?
- Is the tooth a central or lateral (incisor), or a first or second (premolar) or a first, second or third (molar)?
- Is the tooth from the right or left side of the mouth?
- What is the tooth type (incisor, canine, etc.)?
All teeth have a crown and normally have one, two or three roots. The shape of the crown and the number of roots any tooth might have are both usually governed by the site within the oral cavity from where the tooth has come. The crown of a tooth is usually the only part of a tooth that is visible from a clinical examination of the mouth (Figure 1.1). The tip of the root is called the apex and usually has one or more holes (foramen/pl. foramina) through which blood vessels and nerves pass into and out of the dental pulp.
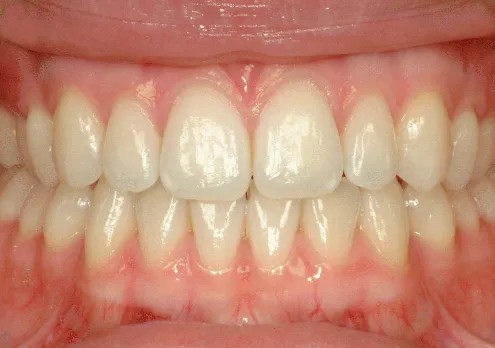
Figure 1.1 Clinical photograph of a normal healthy dentition, gingivae and oral mucosa.
(Source: Dr Rachael McKeown. Reproduced with permission of Dr McKeown)
There are two arches within the oral cavity – an upper or maxillary arch and a lower or mandibular arch (Figures 1.1 to 1.3). The upper arch may be named the maxillary arch, since the roots of the maxillary or upper teeth can be found attached to the upper jaw bone – the maxilla. Likewise, the lower arch may be named the mandibular arch, since the roots of the mandibular or lower teeth can be found attached to the lower jaw bone – the mandible. An anterior (front) view and a lateral (side) view of a human skull can be seen in Figures 1.2 and 1.3.
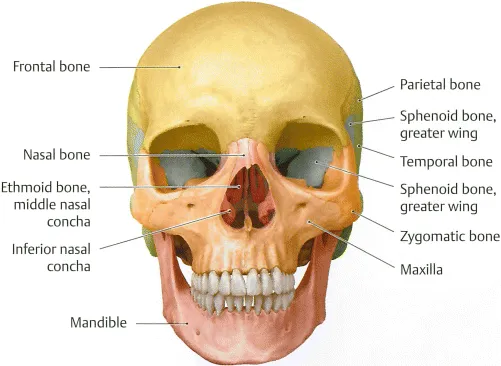
Figure 1.2 Illustrates an anterior (front) view of the human skull. From Head and Neck Anatomy for Dental Medicine. 2010. Ed. EW Baker. Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.
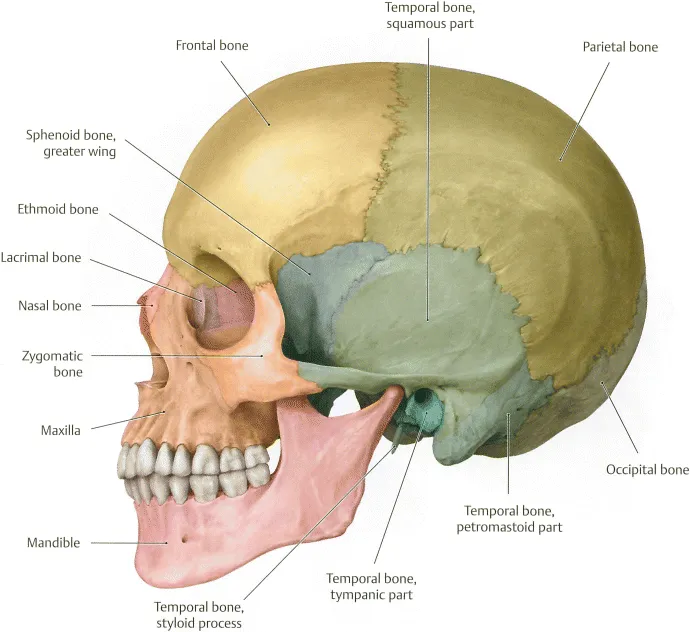
Figure 1.3 Illustrates a lateral (side) view of the human skull. From Head and Neck Anatomy for Dental Medicine. 2010. Ed. EW Baker. Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.
The permanent dentition consists of 32 teeth:
- 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 12 molars The primary dentition consists of 20 teeth:
- 8 incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars
Descriptive Terms
Remember when viewing a patient, you would refer to the upper right, for example, as the patient's upper right and not your right! The midline of the two arches is a common reference point – this is the line dividing right and left central incisors – see Figures 1.1 and 1.2.
The dentition may be split into either four quadrants or six sextants. Both terms are commonly used within clinical dentistry. When the dentition is split into quadrants, each “quadrant” will normally contain a maximum of eight permanent teeth or five primary teeth – a quarter of the dentition. In the case of the permanent dentition, this is made up of two incisors and one canine (which make up the anterior teeth) and two premolars and three molars (which make up the posterior teeth). In the case of the primary dentition, this is made up of two incisors and one canine (the anterior teeth) and two molars (the posterior teeth). The quadrants are referred to as upper right (UR) and upper left (UL), and lower right (LR) and lower left (LL).
The system used in this book will be similar to the Palmer notation (see below). The quadrant will be given first, as above, where UR will be the patient's upper right quadrant, and so on. Permanent teeth are numbered 1–8, with 1 being the permanent central incisor and 8 being the permanent third molar. Primary (or deciduous) teeth are referred to as A–E, with A being the primary central incisor and E being the primary second molar.
Within some clinical disciplines, the dentition is split into six sextants. Each “sextant” may contain approximately one sixth of the teeth – the mandible and the maxilla each contain...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Contributors
- Preface
- About the Companion Website
- Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Human Dentition
- Chapter 2: Oral Embryology
- Chapter 3: Tooth Development
- Chapter 4: Enamel
- Chapter 5: The Pulpo-Dentinal Complex
- Chapter 6: Cementum
- Chapter 7: Alveolar Bone
- Chapter 8: The Periodontal Ligament (PDL)
- Chapter 9: Oral Mucosa
- Chapter 10: The Gingiva
- Chapter 11: Tooth Eruption and Development of the Occlusion
- Chapter 12: The Salivary Glands
- Chapter 13: Saliva
- Chapter 14: Maxillary Sinus
- Chapter 15: The Temporomandibular Joint
- Chapter 16: The tongue
- Chapter 17: Lymph Nodes of the Head and Neck and the Tonsils
- Chapter 18: Dental Plaque and Calculus
- Chapter 19: Dental Caries: The Biological Basis
- Chapter 20: Introduction to Periodontal Disease
- Index
- End User License Agreement