
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Molecular and Quantitative Animal Genetics
About this book
Animal genetics is a foundational discipline in the fields of animal science, animal breeding, and veterinary sciences. While genetics underpins the healthy development and breeding of all living organisms, this is especially true in domestic animals, specifically with respect to breeding for key traits.
Molecular and Quantitative Animal Genetics is a new textbook that takes an innovative approach, looking at both quantitative and molecular breeding approaches. The bookprovides a comprehensive introduction to genetic principles and their applications in animal breeding. This text provides a useful overview for those new to the field of animal genetics and breeding, covering a diverse array of topics ranging from population and quantitative genetics to epigenetics and biotechnology. Molecular and Quantitative Animal Genetics will be an important and invaluable educational resource for undergraduate and graduate students and animal agriculture professionals.
Divided into six sections pairing fundamental principles with useful applications, the book's comprehensive coverage will make it an ideal fit for students studying animal breeding and genetics at any level.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Decoding and Encoding the “DNA” of Teaching and Learning in College Classrooms
Introduction
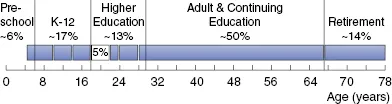
Teaching and Learning: Definitions
| Definitions of “to teach” | |
| 1a | To cause to know something <taught them a trade> |
| 1b | To cause to know how <is teaching me to drive> |
| 1c | To accustom to some action or attitude <teach students to think for themselves> |
| 1d | To cause to know the disagreeable consequences of some action <I'll teach you to come home late> |
| 2 | To guide the studies of |
| 3 | To impart the knowledge of <teach algebra> |
| 4a | To instruct by precept, example, or experience |
| 4b | To make known and accepted <experience teaches us our limitations> |
| 5 | To conduct instruction regularly in <teach school> |
| Definitions of “teaching” | |
| 6 | Teaching: the act, practice, or profession of a teacher |
| 7 | Teaching: something taught (the ideas and beliefs that are taught by a person); especially doctrine <the teachings of Confucius> |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Contributors
- Manuscript Reviewers
- Preface
- 1: Decoding and Encoding the “DNA” of Teaching and Learning in College Classrooms
- Section 1: Quantitative and Population Genetics
- Section 2: Applications of Genetics and Genomics to Livestock and Companion Animal Species
- Section 3: Molecular Genetics of Production and Economically Important Traits
- Section 4: Genetics of Embryo Development and Fertility
- Section 5: Genetics of Animal Health and Biotechnology
- Index
- End User License Agreement