
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Optimization Methods in Metabolic Networks
About this book
Provides a tutorial on the computational tools that use mathematical optimization concepts and representations for the curation, analysis and redesign of metabolic networks
- Organizes, for the first time, the fundamentals of mathematical optimization in the context of metabolic network analysis
- Reviews the fundamentals of different classes of optimization problems including LP, MILP, MLP and MINLP
- Explains the most efficient ways of formulating a biological problem using mathematical optimization
- Reviews a variety of relevant problems in metabolic network curation, analysis and redesign with an emphasis on details of optimization formulations
- Provides a detailed treatment of bilevel optimization techniques for computational strain design and other relevant problems
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
MATHEMATICAL OPTIMIZATION FUNDAMENTALS
This chapter reviews the fundamentals of mathematical optimization and modeling. It starts with a biological network inference problem as a prototype example to highlight the basic steps of formulating an optimization problem. This is followed by a review of some basic mathematical concepts and definitions such as set and function properties and convexity analysis.
1.1 MATHEMATICAL OPTIMIZATION AND MODELING
Mathematical optimization (programming) systematically identifies the best solution out of a set of possible choices with respect to a pre-specified criterion. The general form of an optimization problem is as follows:
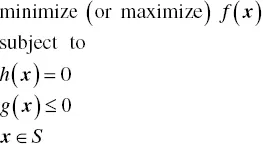
where
- x is a N-dimensional vector referred to as, the vector of variables.
- S is the set from which the elements of x assume values. For example, S can be the set of real, nonnegative real or nonnegative integers. In general, variables in an optimization problem can be continuous, discrete (integer) or combinations thereof. The former is used to capture the continuously varying properties of a system (e.g., concentrations), whereas the latter is used for discrete decision making (e.g., whether or not to eliminate a reaction).
- f(x) is referred to as the objective function and serves as a mathematical description of the desired property of the system that should be optimized (i.e., maximized or minimized).
- and
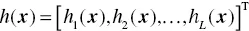 are constraints that must be satisfied as equalities or one-sided inequalities, respectively, and represent the feasible space of decision variables.
are constraints that must be satisfied as equalities or one-sided inequalities, respectively, and represent the feasible space of decision variables.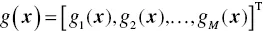
Any vector x that lies in S and satisfies h(x) and g(x) is called a feasible...
Table of contents
- COVER
- TITLE PAGE
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
- PREFACE
- 1 MATHEMATICAL OPTIMIZATION FUNDAMENTALS
- 2 LP AND DUALITY THEORY
- 3 FLUX BALANCE ANALYSIS AND LP PROBLEMS
- 4 MODELING WITH BINARY VARIABLES AND MILP FUNDAMENTALS
- 5 THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF METABOLIC NETWORKS
- 6 RESOLVING NETWORK GAPS AND GROWTH PREDICTIONINCONSISTENCIES IN METABOLIC NETWORKS
- 7 IDENTIFICATION OF CONNECTED PATHS TO TARGET METABOLITES
- 8 COMPUTATIONAL STRAIN DESIGN
- 9 NLP FUNDAMENTALS
- 10 NLP APPLICATIONS IN METABOLIC NETWORKS
- 11 MINLP FUNDAMENTALS AND APPLICATIONS
- APPENDIX A: CODING OPTIMIZATION MODELS IN GAMS
- INDEX
- END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Optimization Methods in Metabolic Networks by Costas D. Maranas,Ali R. Zomorrodi in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Biological Sciences & Biotechnology. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.