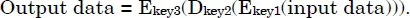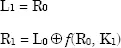![]()
1
Introduction to Cryptography
1.1. The encryption function
The encryption function is the mechanism used to provide a confidentiality service. It enables the modification of a string of bytes (the data being transmitted) in order to make it incomprehensible to anyone who is not authorized to know its content.
Encryption is done using two types of algorithm:
– symmetrical or secret-key algorithms. The same (secret) key is used for encryption and decryption;
– asymmetrical or public key algorithms. Different keys are used for encryption and decryption. The public key (or, conversely, the private key) is used for encryption. The private key (or, conversely, the public key) is used for decryption.
Symmetrical algorithms are grouped into two categories:
– stream cipher algorithms act on bits. A stream cipher generally consists of an exclusive OR or XOR (eXclusive OR) operation between data issued by a pseudo-random number-generator and the data being transmitted;
– block cipher algorithms act on blocks of between 32 and 512 bits in size.
Asymmetrical algorithms are based on modular exponentiation or an elliptical curve.
Asymmetrical algorithms based on modular exponentiation are not adapted to data encryption because they have the disadvantage of being slow. This is due to the size of the keys used. They are used mainly in the following two scenarios:
– secret-key transport. The secret key is encrypted by the public key and decrypted by the private key. Only the holder of the private key can recover the secret key, which guarantees confidentiality;
– signature. The data digest, calculated using a hash function, is encrypted by the private key and decrypted by the public key. The data source is the only holder of the private key, which guarantees the integrity control of the data received, the authentication of the data source, and the non-repudiation by the client.
Table 1.1 shows a comparison of key sizes depending on whether symmetrical and asymmetrical algorithms are used to obtain an equivalent level of security.
Table 1.1. Comparison of key size depending on algorithm
| 80 | 1,024 | 160 |
| 112 | 2,048 | 224 |
| 128 | 3,072 | 256 |
| 192 | 7,680 | 384 |
| 256 | 15,360 | 512 |
1.1.1. 3DES algorithm
The triple data encryption standard (3DES) algorithm is a symmetrical algorithm by blocks. It strings three successive operations of the DES algorithm on a single 64-bit data block.
Three keys (key1, key2 and key3) are used for encryption, one key per operation. Each 64-bit key contains 56 randomly generated bits and 8 odd parity check bits. Two options are defined for the composition of keys:
– option 1: the three keys (key1, key2 and key3) are different;
– option 2: two keys (key1 and key2) are different; two keys (key1 and key3) are identical.
The 3DES algorithm encryption operation consists of sequencing a DES encryption (E) with the key1, a DES decryption (D) with the key2, and a DES encryption (E) with the key3.
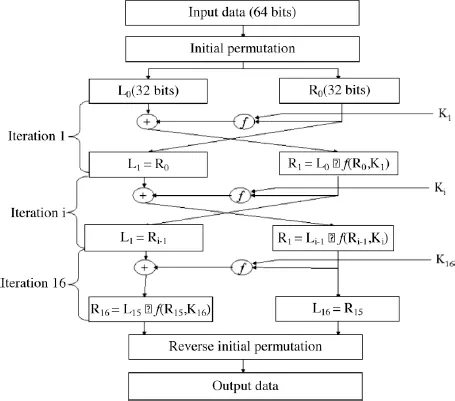
The DES encryption algorithm is shown in Figure 1.1.
Each 64-bit data block is submitted to an initial permutation function. The resulting 64-bit block is then cut into two 32-bit blocks (left block L0 and right block R0).
The DES algorithm is constructed using 16 successive iterations. The first iteration generates, from the two blocks L0 and R0, two blocks L1 and R1 in the following manner:
Figure 1.1. DES algorithm
At each iteration, the same operation is executed:
– left block Li corresponds to right block Ri-1;
– right block Ri is an exclusive OR of left block Li-1 and of the result of an f function applied to right block Ri-1and to Ki deducted from the initial 64-bit key (key1, key2 or key3).
The output of the last iteration is composed of left block L16 and right block R16. Block R16L16 is subjected to a reverse initial permutation.
The f function is described in Figure 1.2.
The E function is u...