
eBook - ePub
Medical Biochemistry
Human Metabolism in Health and Disease
Miriam D. Rosenthal, Robert H. Glew
This is a test
Buch teilen
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Medical Biochemistry
Human Metabolism in Health and Disease
Miriam D. Rosenthal, Robert H. Glew
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Metabolism includes various pathways of chemical reactions; understanding these pathways leads to an improved knowledge of the causes, preventions, and cures for human diseases. Medical Biochemistry: Human Metabolism in Health and Disease provides a concise yet thorough explanation of human metabolism and its role in health and diseases. Focusing on the physiological context of human metabolism without extensive consideration of the mechanistic principles of underlying enzymology, the books serves as both a primary text and resource for students and professional in medical, dental, and allied health programs.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Medical Biochemistry als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Medical Biochemistry von Miriam D. Rosenthal, Robert H. Glew im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Scienze biologiche & Biochimica. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM
1.1 INTRODUCTION
Intermediary metabolism is the name given to the sequences of biochemical reactions that degrade, synthesize, or interconvert small molecules inside living cells. Knowledge of the core metabolic pathways and their interrelations is critical to understanding both normal function and the metabolic basis of most human diseases. Rational interpretation and application of data from the clinical chemistry laboratory also requires a sound grasp of the major metabolic pathways. Furthermore, knowledge of key biochemical reactions in the two dozen or so core metabolic pathways in humans is essential for an understanding of the molecular basis of drug action, drug interactions, and the many genetic diseases that are caused by the absence of the activity of a particular protein or enzyme.
1.1.1 Metabolic Pathways
Metabolism occurs in small discrete steps, each of which is catalyzed by an enzyme. The term metabolic pathway refers to a particular set of reactions that carries out a certain function or functions. The pathway of gluconeogenesis or glucose synthesis, for example, operates mainly during a period of fasting, and its primary function is to maintain the concentration of glucose in the circulation at levels that are required by glucose-dependent tissues such as the brain and red blood cells. Another example of a metabolic pathway is the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, which oxidizes the two carbons of acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) to CO2 and water, thus completing the catabolism of carbohydrates, fats (fatty acids), and proteins (amino acids).
1.1.2 Metabolic Intermediates
Biochemical pathways are comprised of organic compounds called metabolic intermediates, all of which contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Some metabolic intermediates also contain nitrogen or sulfur. In most instances, these compounds themselves have no function. An exception would be a compound such as citric acid, which is both an intermediate in the TCA cycle and a key regulator of other pathways, including oxidation of glucose (glycolysis) and gluconeogenesis.
1.1.3 Homeostasis
Homeostasis refers to an organism’s tendency or drive to maintain the normalcy of its internal environment, including maintaining the concentration of nutrients and metabolites within relatively strict limits. A good example is glucose homeostasis. In the face of widely varying physiological conditions, such as fasting or exercise, both of which tend to lower blood glucose, or following the consumption of a carbohydrate meal that raises the blood glucose concentration, the human body activates hormonal mechanisms that operate to maintain blood glucose within rather narrow limits, 80 to 100 mg/dL (Fig. 1-1). Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) stimulates the release of gluconeogenic hormones such as glucagon and hydrocortisone, which promote the breakdown of liver glycogen and the synthesis of glucose in the liver (gluconeogenesis), followed by the release of glucose into the blood. On the other hand, hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) stimulates the release of insulin, which promotes the uptake of glucose and its utilization, storage as glycogen, and conversion to fat.
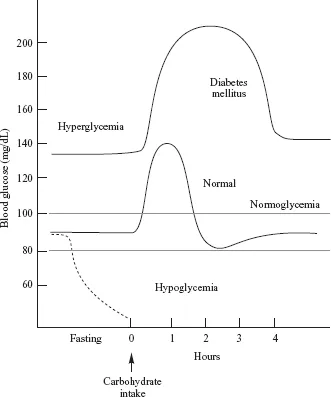
FIGURE 1-1 Changes that occur in the blood glucose concentration in a healthy adult, a person with type II diabetes mellitus, and a person experiencing fasting hypoglycemia. Following ingestion of a carbohydrate-containing meal, there are three features that distinguish the glucose vs. time curve for the person with type II diabetes relative to the healthy adult: (1) the initial blood glucose concentration is higher (approx. 135 vs. 90 mg/dL), (2) the rise in in the glucose level following the meal is greater; and (3) it takes longer for the glucose concentration to return to the fasting glucose level.
Maintenance of the blood calcium concentration between strict limits is another example of homeostasis. The normal total plasma calcium concentration is in the range 8.0 to 9.5 mg/dL. If the calcium concentration remains above the upper limit of normal for an extended period of time, calcium may deposit, with pathological consequences in soft tissues such as the heart and pancreas. Hypocalcemia (a.k.a. tetany) can result in muscle paralysis, convulsions, and even death; chronic hypocalcemia causes rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. The body uses vitamin D and certain hormones (e.g., parathyroid hormone, calcitonin) to maintain calcium homeostasis.
1.2 WHAT DO METABOLIC PATHWAYS ACCOMPLISH?
1.2.1 Generation of Energy
The primary dietary fuels for human beings are carbohydrates and fats (triacylglycerols). The human body also obtains energy from dietary protein and—for some people—ethanol. Metabolism of these fuels generates energy, much of which is captured as the high-energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (Fig. 1-2). The ATP can be used for biosynthetic processes (e.g., protein synthesis), muscle contraction, and active transport of ions and other solutes across membranes.
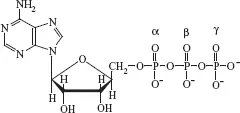
FIGURE 1-2 Structure of adenosine triphosphate.
1.2.2 Degradation or Catabolism of Organic Molecules
Catabolic pathways usually involve cleavage of C–O, C–N, or C–C bonds. Most intracellular catabolic pathways are oxidative and involve transfer of reducing equivalents (hydrogen atoms) to nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) or flavine-adenine dinucleotide (FAD). The reducing equivalents in the resulting NADH or FADH2 can then be used in biosynthetic reactions or transferred to the mitochondrial electron-transport chain for generation of ATP.
1.2.2.1 Digestion.
Before dietary fuels can be absorbed into the body, they must be broken down into simpler molecules. Thus, starch is hydrolyzed to yield glucose, and proteins are hydrolyzed to their constituent amino acids.
1.2.2.2 Glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the oxidation of glucose into the three-carbon compound pyruvic acid.
1.2.2.3 Fatty Acid Oxidation.
The major route of fatty acid degradation is β-oxidation, which accomplishes stepwise two-carbon cleavage of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA.
1.2.2.4 Amino Acid Catabolism.
Breakdown of most of the 20 common amino acids is initiated by removal of the α-amino group of the amino acid via transamination. The resulting carbon skeletons are then further catabolized to generate energy or are used to synthesize other molecules (e.g., glucose, ketones). The nitrogen atoms of amino acids can...