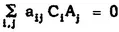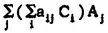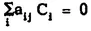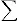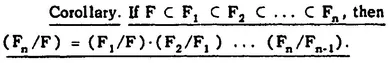A. Extension Fields.
If E is a field and F a subset of E which, under the operations of addition and multiplication in E, itself forms a field, that is, if F is a subfield of E, then we shall call E an extension of F. The relation of being an extension of F will be briefly designated by F ⊂ E. If α, β, γ, ... are elements of E, then by F(α, β, γ, ...) we shall mean the set of elements in E which can be expressed as quotients of polynomials in α, β, γ,... with coefficients in F. It is clear that
F(α, β, γ,...) is a field and is the smallest extension of F which contains the elements α, β, γ, ... . We shall call F(α, β, γ,...) the field obtained after the adjunction of the elements α, β, γ,... to F, or the field generated out of F by the elements α, β, γ,... In the sequel all fields will be assumed commutative.
If F ⊂ E, then ignoring the operation of multiplication defined between the elements of E, we may consider E as a vector space over F. By the degree of E over F, written (E/F), we shall mean the dimension of the vector space E over F. If (E/F) is finite, E will be called a finite extension.
THEOREM 6. If F, B, E are three fields such that F ⊂ B ⊂ E, then
Let A
1 , A
2, ..., A
r be elements of E which are linearly independent with respect to B and let C
1, C
2,..., C
s be elements of B which are independent with respect to F. Then the products C
i A
j where i = 1, 2, ... , s and j = 1, 2, ... , r are elements of E which are independent with respect to F. For if
, then
is a linear combination of the A
j with coefficients in B and because the A, were independent with respect to B we have
for each j. The independence of the C, with respect to F then requires that each a
ij = 0. Since there are r • s elements C
iA
j we have shown that for each r ≤ ( E/B ) and s ≤ ( B/F ) the degree ( E/F ) ≥ r
s. Therefore, ( E/F ) ≥ (B/F) (E/B). If one of the latter numbers is infinite, the theorem follows. If both ( E/B ) and ( B/F ) are finite, say r and s respectively, we may suppose that the A
j and the C
i are generating systems of E and B respectively, and we show that the set of products C
i A
j is a generating system of E over F. Each A
E can be expressed linearly in terms of the A
j with coefficients in B. Thus, A =
B
j A
j. Moreover, each B
j being an element of B can be expressed linearly with coefficients in F in terms of the C
i, i.e., B
j =
a
ij C
i, j = 1, 2, ... , r. Thus, A =
a
ij C
iA
j and the C
iA
j form an independent generating system of E over F.
B. Polynomials.
An expression of the form aoxn + a1xn–1+ ... + an is called a polynomial in F of degree n if the coefficients ao, ... , an are elements of the field F and ao ≠0. Multiplication and addition of polynomials are performed in the usual way3.
A polynomial in F is called reducible in F if it is equal to the product of two polynomials in F each of degree at least one. Polynomials which are not reducible in F are called irreducible in F.
If f(x) = g (x)
h(x) is a relation which holds between the polynomials f (x), g (x), h (x) in a field F, then we shall say that g (x)
divides f(x) in F, or that g (x) is a
factor of f (x). It is readily seen ...