
eBook - ePub
ECG Masters Collection Volume 2
Favorite ECGs from Master Teachers Around the World
Mohammad Shenasa, Mark E. Josephson, N.A. Mark Estes III, Ezra Amsterdam, Melvin Scheinman, Mohammad Shenasa, Mark E. Josephson, N.A. Mark Estes III, Ezra Amsterdam, Melvin Scheinman
This is a test
Buch teilen
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
ECG Masters Collection Volume 2
Favorite ECGs from Master Teachers Around the World
Mohammad Shenasa, Mark E. Josephson, N.A. Mark Estes III, Ezra Amsterdam, Melvin Scheinman, Mohammad Shenasa, Mark E. Josephson, N.A. Mark Estes III, Ezra Amsterdam, Melvin Scheinman
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Over 75 exceptional electrocardiogram case studies curated from the libraries of 60 internationally recognized master teachers of ECG interpretation are brought together in this one-of-a-kind resource for student and teacher alike.
Organized by disease type, ECG case studies are presented in a clinical context followed by questions and discussion. Medical students, residents, fellows, physicians — anyone who is involved in caring for patients with various cardiovascular diseases and other systemic pathologies — will find this unique collection with a global perspective useful and practical in developing the skills necessary to reading ECGs.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist ECG Masters Collection Volume 2 als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu ECG Masters Collection Volume 2 von Mohammad Shenasa, Mark E. Josephson, N.A. Mark Estes III, Ezra Amsterdam, Melvin Scheinman, Mohammad Shenasa, Mark E. Josephson, N.A. Mark Estes III, Ezra Amsterdam, Melvin Scheinman im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Médecine & Cardiologie. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
SECTION 1
Introduction to the Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram
CASE
1.1
The first and most important step in ECG interpretation is the differentiation between “normal” and “abnormal.”
The second step consists of differentiation between the various abnormal ECG patterns and their correlation with known pathologic conditions. In particular, the recent discoveries with small, subtle, significant markers for adverse events such as early repolarization, Brugada-type ECGs, and other channelopathies.
Information about the ECG in disease is much more complex than knowledge of normal variation. Yet, it is in the differentiation between normal and abnormal that difficulties in ECG interpretation frequently arise.
Below are two examples of normal ECGs.
Heart rate: 64 bpm
PR interval: 154 ms
QRS duration: 98 ms
QT/QTc: 406/415 ms
Normal ST-T wave patterns
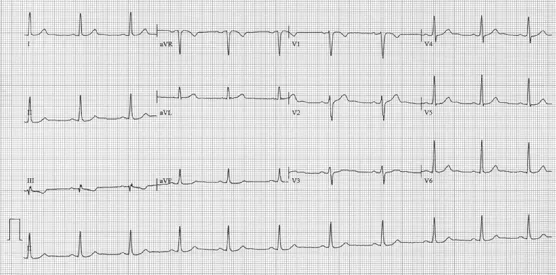
Figure 1.1.1
Heart rate: 80 bpm
PR interval: 148 ms
QRS duration: 92 ms
QT/QTc: 364/420 ms
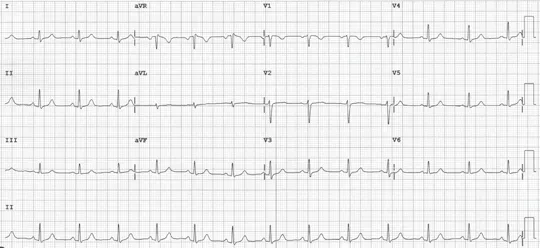
Figure 1.1.2
It is important to have a systematic approach when analyzing and interpreting of ECGs.
1. Baseline findings in sinus rhythm.
2. Observations during tachycardias.
3. Analysis of the changes of the cardiographic morphologies (transient changes).
4. Mode of spontaneous initiation and termination.
5. Maneuvers during tachycardias.
In a stepwise approach to ECG or rhythm analysis, one should determine the rate of the tachycardia (fast or slow), the QRS duration (wide or narrow) and morphology, and the relationship of the P wave to the QRS, whether it is before, during, or after, and if there is a one-to-one relationship between the P wave and the QRS.
Other important points regarding interpretation of the ECG.
1. Determine the origin and initiation of cardiac arrhythmias.
2. Look for myocardial ischemia and infarction.
3. Evidence of electrolyte imbalance and reversible causes.
4. Systemic and myocardial disorders.
5. Measure; do not eyeball the intervals.
6. Focus on the zone of transition.
References
1. Wellens HJ, Gorgels AP. The electrocardiogram 102 years after Einthoven. Circulation. 2004;109(5):562–564.
2. Yong CM, Froelicher V, Wagner G. The electrocardiogram at a crossroads. Circulation. 2013;128(1):79–82.
3. Stern S. Electrocardiogram: Still the cardiologist’s best friend. Circulation. 2006;113(19):e753–e756.
SECTION 2
Conduction Disturbances: Sinus Node Disease/Sick Sinus Syndrome, AV Conduction Disturbances, AV Blocks,
Bundle Branch Blocks, and Fascicular Blocks
CASE
2.1
Patient History
Two cases are shown in Figure 2.1.1. The first is from a 68-year-old female with severe aortic stenosis who underwent aortic replacement three days prior to the date that the rhythm strip (Panel A) was obtained. Her surgery was uneventful, and her native valve was replaced with a 21-mm Medtronic Mosaic tissue valve. The second case is an 84-year-old male with a 10-day history of recurrent syncope who was admitted to the hospital.
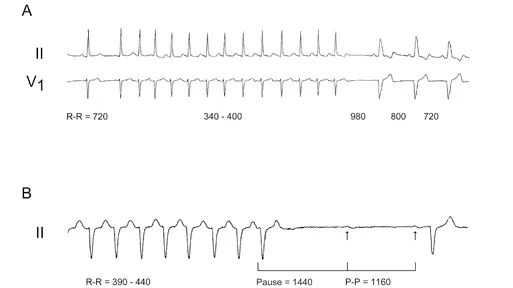
Figure 2.1.1 The occurrence of block after termination of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). Panel A shows a non-sustained run of narrow QRS complex atrial tachycardia (AT) followed by sinus beats exhibiting left bundle branch block (LBBB). Panel B depicts termination of a wide QRS complex AT followed by a 1440-ms pause and then a blocked sinus beat. The subsequent sinus beat is conducted with first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block (PR interval of 300 ms) and a QRS complex similar to that during AT. All of the intervals are in ms. The paper speed is different in these two panels.
The rhythm strip (Panel B) was obtained from the patient one day after admission.
Question
What is the probable mechanism of block in Figure 2.1.1A and B?
1. Pause-dependent block
2. His-Purkinje system (HPS) fatigue phenomenon
3. Functional block in the HPS
4. Potent vagal stimulation
Answer
The correct answer is A. The common theme in these two cases is the termination of a run of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), followed by a pause before the arrival of the next sinus (P wave) beat. Subsequently, the P wave is conducted with LBBB in panel A and bilateral BBB in panel B. In other words, the occurrence of block is preceded by a sudden short-to-long input to the AV conduction system. It should be mentioned that the SVT, in both cases, is most likely AT with narrow QRS complex in Case 1; and with RBBB and left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) (bifascicular block) in Case 2 (Figure 2.1.2). Case 2 suddenly developed third-degree AV block later during the same hospital course (Figure 2.1.3).
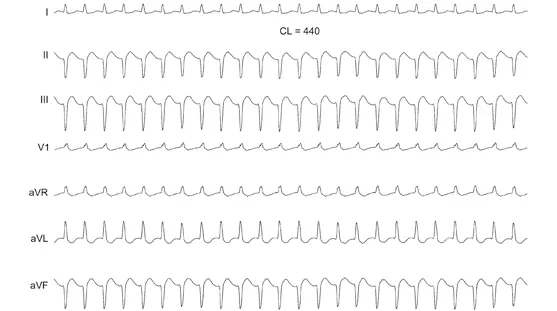
Figure 2.1.2 Sustained AT. Seven-lead ECG of a sustained episode of AT with a cycle length (CL) of 440 ms is shown. The QRS complex is 120 ms with RBBB and LAFB present.
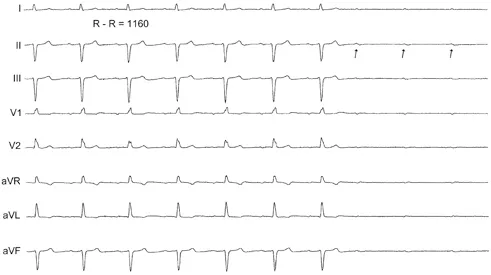
Figure 2.1.3 Spontaneous third-degree AV block...