
Gynaecology in Primary Care
A Practical Guide
Anita Sharma
- 272 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Gynaecology in Primary Care
A Practical Guide
Anita Sharma
Über dieses Buch
Gynaecology in Primary Care comes at a time of great change in health service delivery. General practice is facing the challenges of developing Clinical Commissioning Groups, providing an ever greater range of primary care services and implementing NICE guidelines, whilst CCGs through their members will be under a legal duty to innovate. From a provider perspective, the book equips general practitioners with up-to-date knowledge of common gynaecological conditions, suggestions of best practice with regard to management and investigations to be undertaken within primary care, and guidelines for onward referral, where this is appropriate and necessary. From a commissioning perspective it provides an invaluable resource to CCGs, to inform their future pathways for gynaecology care. This highly practical book delivers the main aim of the RCP report - to ensure best care for female patients in the setting of their choice and where possible to develop streamlined one-stop services in primary care so that women do not have to take time off from their work and family commitments. It is ideal for general practitioners needing to be inspired and informed, and is also highly recommended for other healthcare professionals and medical students with an interest in women's health. 'Optimal patient care requires many connected features to synchronise effectively. This book describes how this could be achieved by focusing attention on well-crafted, evidencebased clinical pathways. This book advances our thinking on how we connect clinical, system and patient level perspectives on optimal care management.' Denis Gizzi, in his Foreword 'Written by a highly regarded, experienced and practicing GP, who has taken on the role as Clinical Director on behalf of the CCG for this programme area, this book is a valuable asset for both practicing GPs and developing CCGs to ensure that gynaecology services effectively commission, maximise the health of the population, improve the experience of the patient, and improve value for money.' Kath Wynne-Jones, in her Foreword 'An excellent guide to the management of gynaecological problems in primary care for not only clinicians in training, but for more experienced clinicians who look for straightforward and easily accessible advice to support their clinical management decisions. Look no further than this textbook. Dr Sharma's textbook will be a boon to developing organisations in delivering world-class services.' Dr Ian Wilkinson, in his Foreword
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
1
Dysmenorrhoea
Pathophysiology of primary dysmenorrhoea:
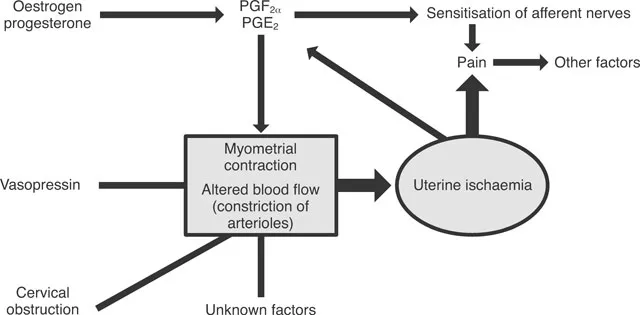
www.sogc.org/guidelines/public/169E-CPG-December2005.pdf
Prevalence
Risk factors
- smoking
- early menarche
- heavy menstrual bleed
- prolonged menstrual bleed
- strong family history
- obesity
- age (symptoms are more pronounced in adolescents than in older women)7
- lower socioeconomic groups4
- frequent lifestyle changes, less social support and stressful relationships.9