
eBook - ePub
Data Structures using C
A Practical Approach for Beginners
Amol M. Jagtap, Ajit S. Mali
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 342 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Data Structures using C
A Practical Approach for Beginners
Amol M. Jagtap, Ajit S. Mali
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
The data structure is a set of specially organized data elements and functions, which are defined to store, retrieve, remove and search for individual data elements. Data Structures using C: A Practical Approach for Beginners covers all issues related to the amount of storage needed, the amount of time required to process the data, data representation of the primary memory and operations carried out with such data. Data Structures using C: A Practical Approach for Beginners book will help students learn data structure and algorithms in a focused way.
- Resolves linear and nonlinear data structures in C language using the algorithm, diagrammatically and its time and space complexity analysis
-
- Covers interview questions and MCQs on all topics of campus readiness
-
- Identifies possible solutions to each problem
-
- Includes real-life and computational applications of linear and nonlinear data structures
-
This book is primarily aimed at undergraduates and graduates of computer science and information technology. Students of all engineering disciplines will also find this book useful.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Data Structures using C als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Data Structures using C von Amol M. Jagtap, Ajit S. Mali im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Computer Science & Programming Algorithms. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
1 Fundamental Principles of Algorithm and Recursion
DOI: 10.1201/9781003105800-1
1.1 Algorithm, Its Pseudo-Code Representation and FlowChart
1.1.1 Algorithm Definition
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem. A sequential solution to any program that is scripted in any natural language is called as an algorithm. The algorithm is the first step of the solving process. After the problem analysis, the developer writes the algorithm for this problem. It is largely used for data processing, computing and other related computer and mathematical operations.
The algorithm must satisfy the following five conditions:
- Input: Zero, one or more quantities are externally provided.
- Output: The algorithm produces at least one output as a result.
- Definiteness: Each statement must be clear, specific, and unambiguous.
- Finite: The algorithm should conclude after a limited number of steps.
- Effectiveness: Every statement must be very fundamental so that it can be carried out by any individual using only paper and pencil.
1.1.2 Pseudo-Code Representation
The word “pseudo” means “fake,” so “pseudo-code” means “fake code”. Pseudo-code is an informal language used by programmers to develop algorithms. Pseudo-code describes how you would implement an algorithm without getting into syntactical details. It uses the structural conventions of a formal programming language but is proposed for human reading rather than machine reading. It is used to create an overview or outline of a program. System designers write pseudo-code to make sure the programmer understands a software project’s requirements and aligns the code accordingly. The pseudo-code contains no variable declaration.
The pseudo-code follows certain standard loop structures as follows:
- FOR… ENDFOR
- WHILE… ENDWHILE
Certain terms also exist for standard conditional clauses:
- IF… ENDIF
- WHILE… ENDWHILE (this is both a loop and a conditional clause by the way)
- CASE… ENDCASE
The pseudo-code cannot be compiled within an executable program.
Example in C code:
if (I < 10) { I++; } Therefore, its respective pseudo-code is:
If I is less than 10, increment I by 1.
Benefits of pseudo-code:
- Pseudo-code is understood by every programming language developer like Java or C#. Net developer, etc.
- Programming languages are difficult to read for most people, but pseudo-code permits non-programmers, such as business analysts, end user or customer to review the steps to approve the projected pseudo-code that matches the coding specifications.
- By drafting the code in human language first, the programmer protects from omitting an important step.
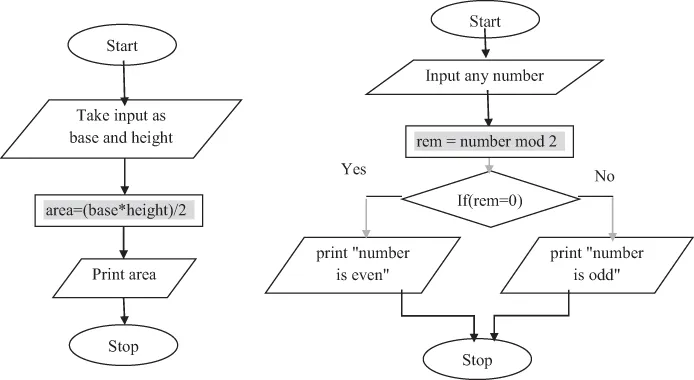
Example 1.1: Algorithm for Identifying the Area of a Triangle
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Take input as the base and the height of the user
- Step 3: Area = (base * height)/2
- Step 4: Print area of triangle
- Step 5: Stop.
Example 1.2: An Algorithm Used to Determine Number Is Odd or Even
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Enter any input number
- Step 3: Reminder = number mod 2
- Step 4: If reminder = 0, then
Print "number is even" Else Print "number is odd" End if
- Step 5: Stop.
1.1.3 Flowchart
The graphical representation of any program is referred to as flowcharts. A flowchart is a kind of diagram that represents an algorithmic program, a workflow or operations. A flowchart aims to provide people with a common language to understand a project or process. Developers often use it as a program-planning tool for troubleshooting a problem. Each flowchart provides the solution to a specific problem. There are a few standard graphics symbols, which are used in the flowchart as follows:
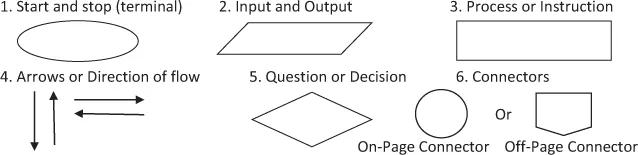
- Start and Stop or Terminal The circular rectangles or oval symbol indicates where the flowchart starts and ends.
- Input and Output The parallelogram symbol denotes input or output operations in the flowchart.
- Process or Instruction The rectangle represents a process like computations, a mathematical operation or a variable assignment operation, etc.
- Arrows or Direction of Flow Arrows or direction of flow represents the flow of the sequence of steps and direction of a process.
- Question or Decision The diamond symbol is used as a representation of the true or false statement tested in a decision symbol.
- Connector A flowchart is divided into two or more smaller flowcharts, consistent with project requirements. This connector is most often used when a flowchart does not fit on a single page or has to be split into sections. A connector symbol, which is a small circle called an On-Page Connector, with a number inside it, allows you to connect two flowcharts on the same page.A connector symbol that looks like a pocket on a shirt, called off-page connector allows you to connect to a flow diagram on another page.
Guidelines for developing flowcharts:
Here are a couple of things to keep in mind when designing and developing a flowchart:
- The arrows should not intersect during the design of a flowchart.
- Processes or activities take place from top to bottom or from left to right in general.
- The on-page connectors are referenced using digits in general.
- Off-page connectors are referenced using alphabets generally.
- The flowchart may have only one beginning symbol and a one-stop symbol.
- The shapes, lines and texts of a flowchart need to be consistent.
Pros and cons of flowcharts:
Advantages of flowchart:
- Flowcharts are one of the best ways of documenting programs.
- Flowcharts are easier to understand compared to algorithms and pseudo-codes.
- It helps us to debug and analyze processes.
- It helps us understand how to think or make decisions to formulate the problem.
Disadvantages of flowchart:
- Manual tracking is needed to verify the accuracy of the paper flowchart.
- Modification of the flowchart is sometimes time-consuming.
- It is difficult to display numerous branches and create loops in the flowchart.
- A simple modification of the problem logic can result in a complete redesign of the flowchart.
- It is very difficult to draw a flowchart for huge and complicated programs.
Example: Draw a flowchart to find area of triangle and odd or even number:
1.2 Abstract Data Type
Abstract data type (ADT) is a type or class of objects whose behavior is determined by a set of values and a set of functions. The definition of ADT only refers to the transactions that need to be performed, but not the way these transactions will be implemented. It does not specify how the data will be organized in memory and what algorithms will be used for the implementation of those operations. It is called “abstract” because it provides an independent perspective from the implementation. The process of supplying only the essentials and concealing details is known as abstraction.
The programmer who has used the data type may not know that how data type is implemented...