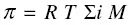![]()
© IWA Publishing 2017. Rodrigo Valladares Linares, Zhenyu Li, Menachem Elimelech, Gary Amy and Hans Vrouwenvelder. Recent Developments in Forward Osmosis Processes. DOI: 10.2166/9781780408125_001
Part 1
Introduction
![]()
Chapter 1.1
Population distribution and water scarcity
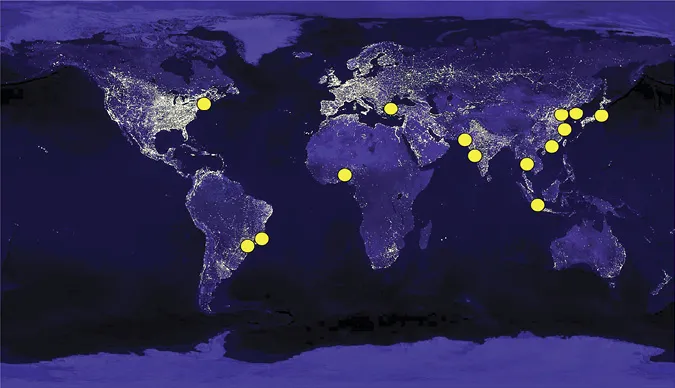
Globally, the level of urbanization has significantly increased during the last six decades. In 2010, urban areas comprised 3.5 billion people, or 50.5 per cent of the world’s population (United Nations, 2011). Due to the development of coastal regions in many countries, two-fifths of cities with populations of 1 million to 10 million people are located near coastlines (Tibbetts, 2002). Moreover, 14 of the largest 17 cities in the world are situated along coasts (Figure 1.1.1) (Creel, 2003b).
Figure 1.1.1 Fourteen of the world’s largest cities are located along the coast (indicated in orange), which translates into an opportunity to integrate drinking water and wastewater management, especially in water-stressed areas (Creel, 2003) (image adapted from: NASA (2000)).
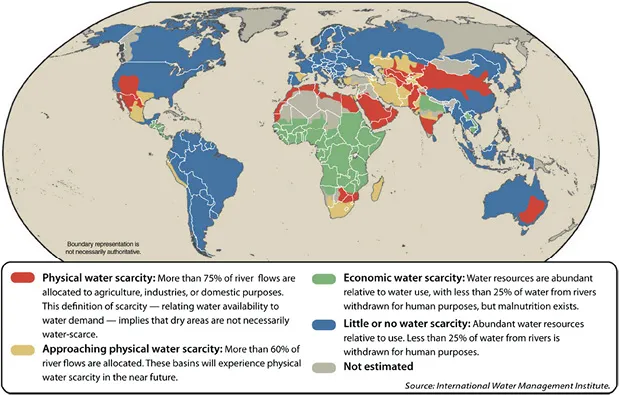
With increasing population growth, the demand for clean water is also increasing. Under an average economic growth scenario and when no efficiency gains are assumed, global fresh water demand will increase 53% from 2009 to 2030, from 4.5 trillion m3 to 6.9 trillion m3 (The Barila Group et al. 2009), with a proportionally greater deficit in many developing countries. This situation will leave between 2.4 billion and 3.2 billion people under water-scarce or water-stressed conditions by year 2025, four-folding the number of people that lived in areas with limited fresh water availability at the beginning of the 20th century. Water shortage is likely to grow especially acute in the Middle East and much of Africa (Engelman et al. 2000), as well as vast areas in Australia, China, India and Mexico (Figure 1.1.2), directly associated with the physical absence of additional fresh water resources to cover their demand. Besides the amount of water itself, the quality must comply with the minimum standards set by each country’s regulations to be considered as potable; diarrheal disease alone is responsible for the death of 1.8 million people every year, and it was estimated that 88% of these cases are attributable to unsafe water supply, sanitation and hygiene (Prüss-Üstün & Corvalá, 2004).
Figure 1.1.2 Projected global water scarcity by 2025 (international water management institute).
Human population distribution along the coasts represents a great challenge in terms of water management, due to the contamination of surface and ground water (basins, aquifers, rivers, etc.), limited fresh water sources in some areas, and more stringent environmental regulations that restrict the use of certain water resources. Therefore, a comprehensive strategy for the management of water resources is crucial for the sustainable development of these areas (Li et al. 2014).
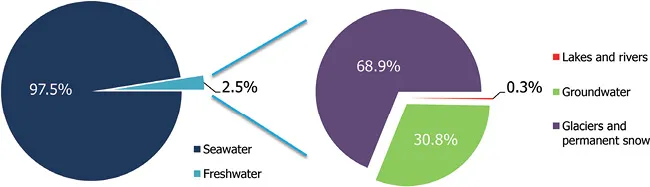
Since more than 97% of the water in the world is seawater (Figure 1.1.3), desalination technologies have the potential to solve the fresh water crisis, particularly in coastal areas. The most used desalination technique nowadays is reverse osmosis, where a membrane is used as a physical barrier to separate the salts from the water, using high hydraulic pressure (Amjad, 1993). Nevertheless, the use of pressure imposes a high cost on operation of these systems, besides the known persistent fouling problems associated with membrane filtration systems (Ridgway & Flemming, 1996; Shannon et al. 2008; Vrouwenvelder et al. 2008).
Figure 1.1.3 Total water distribution in the world (UNESCO, 1999).
Research has identified the potential for hybrid forward osmosis/reverse osmosis (FO/RO) systems for several applications, including sweater desalination (Choi et al. 2009), to reduce the cost and fouling propensity of producing fresh water from impaired-quality water sources (Chang et al. 2002; Achilli et al. 2009; Boo et al. 2013). Recently, studies have shown the potential of these systems to produce low cost high quality fresh water using low pressure desalination, while simultaneously recovering impaired water from a recycled feed water (Cath et al. 2009; Yangali-Quintanilla et al. 2011). Nevertheless, there are concerns about the use of FO membranes as a barrier for rejecting micropollutants and nutrients from the wastewater, besides the inevitable fouling problems that can occur during the filtration process, when the membrane is submerged in the recycled feed water, resulting in a poor water flux and an increase in the operational cost due to membrane cleaning.
1.1.1 OSMOTIC MEMBRANE PROCESSES
Osmosis is defined as the transport of water through a semipermeable membrane caused by a difference in osmotic pressure for the solutions on both sides of the membrane. The osmotic pressure is related to the concentration of dissolved ions in solution and the temperature (Cath et al. 2009).
Osmotic pressure (π) can be calculated using the van’t Hoff equation (van’t Hoff, 1887):
where i is the dimensionless van’t Hoff factor for the specific ion, M is the molarity of the specific ion, R is the gas constant (0.08206 L ⋅ atm ⋅ mol−1 ⋅ K−1), and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
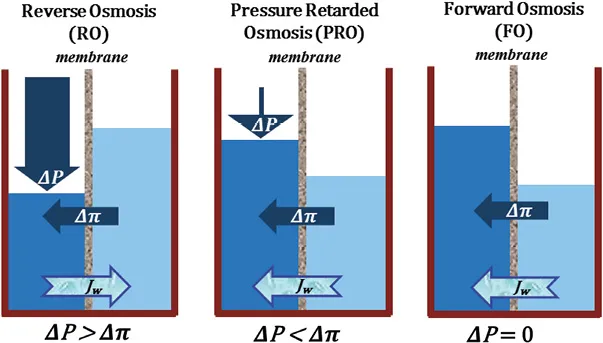
The most common applied membrane filtration processes are reverse osmosis (RO), pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) and forward osmosis (FO), also known as osmosis or direct osmosis, are shown in Figure 1.1.4.
Figure 1.1.4 Osmotic processes in membrane filtration. ΔP – applied hydraulic pressure; Δπ – osmotic pressure difference between the two solutions; Jw – water flux.
RO occurs when the osmotic pres...