
eBook - ePub
Ancient Egypt
David Pickering
This is a test
Buch teilen
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Ancient Egypt
David Pickering
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Ancient Egypt als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Ancient Egypt von David Pickering im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Histoire & Histoire de l'Égypte antique. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Thema
HistoirePART ONE
The land of the pharaohs
The emergence of civilization in Egypt depended heavily upon the region’s geographical features. Most important of these was the Nile, the longest river in the world, on the banks of which the first Egyptian settlements and cities evolved and developed.
THE VALLEY OF THE NILE
Little rain falls in the north-west corner of Africa where Egypt is located. Without the River Nile, Egypt would be little more than an uninhabitable hot sandy desert, and there would never have been an ancient Egyptian civilization, which sprang up along its banks.
Many thousands of years ago, Egypt was mainly swampland, but as the climate grew drier the Nile retreated, leaving a strip of fertile soil on both banks. This soil was refreshed each year by the floodwaters that covered the fields with rich black mud in which plants grew readily. The early settlers learned to farm this land and to construct canals and dykes to regulate the flow of water. Towns sprang up along the length of the Nile, the river providing the people with drinking water as well as water for crops.
THE BLACK LAND
The Egyptians called the fertile land on which they built their towns Kemet, meaning ‘black land’. The rest of the country was known as the Red Land. The deserts of the Red Land were very important because they protected the early Egyptians from attacks by neighbouring civilizations, as few armies were willing to cross such desolate waterless wastes.
Sacred river
The ancient Egyptians understood that their lives depended heavily upon the Nile. In their paintings, heaven was often depicted as fertile land surrounded by water.
The waterfalls and rapids of the Nile south of Egypt also hindered invasion from lower down the river. The Egyptians themselves transported their soldiers up or down the Nile to fight off any invaders. The Nile was also vital for trade, providing access to the waters of the Mediterranean Sea in the north and to central Africa in the south.
EGYPT AND THE WORLD
The geographical location of Egypt at the point where Africa meets the Middle East was to prove vital to its development into a great civilization. The natural resources of the region, which included minerals and building stone from the desert as well as crops from the fertile fields beside the Nile, could be transported either by river or across the desert to be traded with neighbouring peoples.
Access to the Mediterranean and to the Red Sea enabled Egyptian merchants sailing out of the Nile to take their goods anywhere in the known world.
EMPIRES OF THE PHARAOHS
With economic development came great wealth and political influence. The physical size of Egypt’s empire varied from age to age, sometimes extended by military conquest – at its greatest extent, it included large parts of northern Africa and Palestine among other neighbouring regions. The relatively close geographical links with the centres of Greek and Roman civilization were particularly important in the later history of ancient Egypt.
Centres of civilization
The most important centres of ancient Egyptian civilization were the traditional capitals of Memphis in the north (including the pyramids at Giza, near modern Cairo) and Thebes in the south (with such associated sites as Karnak, Luxor and the Valley of the Kings). The last capital of ancient Egypt, Alexandria (on the Nile delta in the far north of the country) was not built until the fourth century BC.
Aegyptus to Egypt
The word Egypt is derived from the Greek name for the country: Aegyptus. In Greek mythology, Aegyptus was a descendant of the heifer maiden lo and was the country’s first ruler.
Ancient Egypt
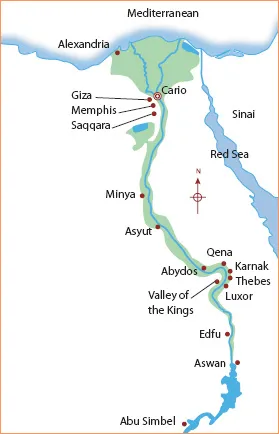

Egyptian civilization was concentrated on the banks of the Nile, from its delta extending 1000km (650 miles) south to Aswan.
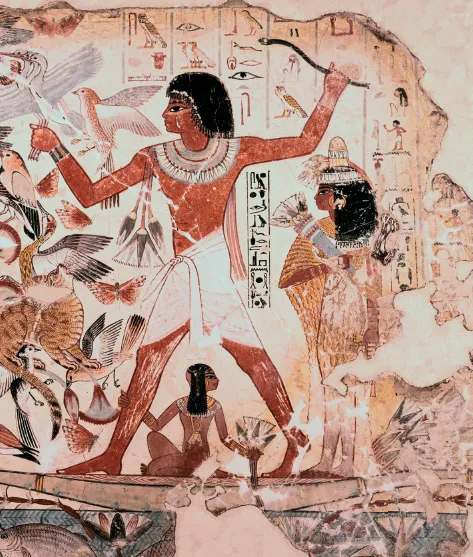

Egyptian life
A man and his family hunting wild birds on the River Nile, which was always at the heart of ancient Egyptian civilization.
A man and his family hunting wild birds on the River Nile, which was always at the heart of ancient Egyptian civilization.
PART TWO
The history of ancient Egypt
The civilization of ancient Egypt lasted some 3000 years, longer than any other civilization in world history. At its peak it was remarkable for its cultural, religious and economic achievements. Historians traditionally subdivide this era into a dozen or so periods covering 30 ruling dynasties, beginning around 3000 BC and ending with the Roman invasion in the first century AD.
PREDYNASTIC PERIOD
c. 8000 BC The drying-out of the Sahara caused by a change in the climate, and possibly over-grazing, forces the population to concentrate in the Nile Valley. Egyptian farmers become the first to herd domesticated cattle and other livestock.
c. 6000 BC The first simple single-sailed ships are built. Stone tools are replaced by tools made of metal. Trades include tanning and basket-weaving.
c. 5000 BC Two broadly similar civilizations develop, one in the south of the country (Upper Egypt) and one in the north (Lower Egypt).
c. 4000 BC The first large stone buildings are constructed. Advances are also made in the fields of alchemy, cosmetics, music, medicine and pottery. The building of underground tombs containing grave goods anticipates later burial practices.
c. 3500 BC The Egyptians invent senet, the world’s oldest known board game.
The first people came to Egypt from central Africa some time between 100,000 and 50,000 BC. Archaeological finds suggest that Egypt’s original hunter-gatherers learned to grow grain beside the Nile by 10,000 BC. It was on this prosperous agricultural economy that the country’s later greatness was to depend.
FLINT TOOLS
The first Egyptians belonged to wandering tribes who relied upon the use of flint tools. As the centuries passed they gradually settled in the Nile Valley, living by hunting animals and fishing.
CRAFTS AND TRADE
Around this time the Egyptians also developed skills in using stone, copper, clay, wood and leather and established thriving craft industries. The building of simple papyrus boats promoted links between communities and enabled traders to travel up and down the Nile. Villages and towns sprang up along the length of the river, from the delta in the north to what is now Aswan in the south, each with their own tribal chief, gods, burial customs and artistic styles.
UPPER AND LOWER EGYPT
Little is known about the history of these early kingdoms, though several rulers are known by name, among them Crocodile, Scorpion I, Scorpion II, Iryhor and Ka. The eventual merging of these two kingdoms, which shared a common language an...