
Problems in Probability
T M Mills
- 192 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Problems in Probability
T M Mills
Über dieses Buch
This is a book of problems in probability and their solutions. The work has been written for undergraduate students who have a background in calculus and wish to study probability.
Probability theory is a key part of contemporary mathematics. The subject plays a key role in the insurance industry, modelling financial markets, and statistics in general — including all those fields of endeavour to which statistics is applied (e.g. health, physical sciences, engineering, economics, social sciences). Every student majoring in mathematics at university ought to take a course on probability or mathematical statistics. Probability is now a standard part of high school mathematics, and teachers ought to be well versed and confident in the subject. Problem solving is important in mathematics. This book combines problem solving and probability.
Contents:
- Sets, Measure and Probability
- Elementary Probability
- Discrete Random Variables
- Continuous Random Variables
- Limit Theorems
- Random Walks
Readership: Undergraduates and lecturers in probability.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
PART 1
Problems

Chapter 1
Sets, measure and probability
1.1 Notes
Logic
Sets

Measure and probability
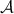
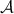
1.2 Problems
According to Rényi [54, p.26] there are 18 different subsets that can be constructed in this way having started with n = 3 distinct subsets A, B, C. Indeed,