
eBook - ePub
Vector Geometry
Gilbert de B. Robinson
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 192 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Vector Geometry
Gilbert de B. Robinson
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
This brief undergraduate-level text by a prominent Cambridge-educated mathematician explores the relationship between algebra and geometry. An elementary course in plane geometry is the sole requirement for Gilbert de B. Robinson's text, which is the result of several years of teaching and learning the most effective methods from discussions with students.
Topics include lines and planes, determinants and linear equations, matrices, groups and linear transformations, and vectors and vector spaces. Additional subjects range from conics and quadrics to homogeneous coordinates and projective geometry, geometry on the sphere, and reduction of real matrices to diagonal form. Exercises appear throughout the text, with complete answers at the end.
Topics include lines and planes, determinants and linear equations, matrices, groups and linear transformations, and vectors and vector spaces. Additional subjects range from conics and quadrics to homogeneous coordinates and projective geometry, geometry on the sphere, and reduction of real matrices to diagonal form. Exercises appear throughout the text, with complete answers at the end.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Vector Geometry un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Vector Geometry de Gilbert de B. Robinson en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Mathematics y Analytic Geometry. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
Categoría
MathematicsCategoría
Analytic Geometry1
LINES AND PLANES
1.1 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The study of geometry is essentially the study of relations which are suggested by the world in which we live. Of course our environment suggests many relations, physical, chemical and psychological, but those which concern us here have to do with relative positions in space and with distances. We shall begin with Euclidean geometry, which is based on Pythagoras’ theorem:
The square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
The statement of this fundamental result implies a knowledge of length and area as well as the notion of a right angle. If we know what we mean by length and may assume its invariance under what we call “motion,” we can construct a right angle using a ruler and compass. We define the area of a rectangle as the product of its length and breadth. To be rigorous in these things is not desirable at this stage, but later on we shall consider a proper set of axioms for geometry.
While the Greeks did not explicitly introduce coordinates, it is hard to believe that they did not envisage their usefulness. The utilization of coordinates was the great contribution of Descartes in 1637, and to us now it is a most natural procedure. Take an arbitrary point O in space, the corner of the room, for instance, and three mutually perpendicular coordinate axes. These lines could be the three lines of intersection of the “walls” and the “floor” at O; the planes so defined we call the coordinate planes. In order to describe the position of a point X, we measure its perpendicular distances from each of these three planes, denoting the distances x1, x2, x3 as in Figure 1.1 It is important to distinguish direction in making these measurements. Any point within the “room” has all its coordinates (x1, x2, x3) positive; measurements on the opposite side of any coordinate plane would be negative. Thus the following eight combinations of sign describe the eight octants of space about O:
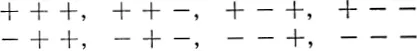
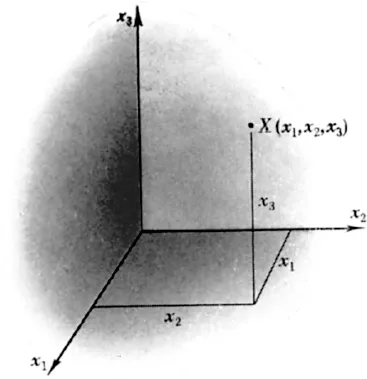
FIG. 1.1
We may describe the points on the “floor” by saying that x3 = 0; this is the equation of this ...