
eBook - ePub
Vector Geometry
Gilbert de B. Robinson
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 192 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Vector Geometry
Gilbert de B. Robinson
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This brief undergraduate-level text by a prominent Cambridge-educated mathematician explores the relationship between algebra and geometry. An elementary course in plane geometry is the sole requirement for Gilbert de B. Robinson's text, which is the result of several years of teaching and learning the most effective methods from discussions with students.
Topics include lines and planes, determinants and linear equations, matrices, groups and linear transformations, and vectors and vector spaces. Additional subjects range from conics and quadrics to homogeneous coordinates and projective geometry, geometry on the sphere, and reduction of real matrices to diagonal form. Exercises appear throughout the text, with complete answers at the end.
Topics include lines and planes, determinants and linear equations, matrices, groups and linear transformations, and vectors and vector spaces. Additional subjects range from conics and quadrics to homogeneous coordinates and projective geometry, geometry on the sphere, and reduction of real matrices to diagonal form. Exercises appear throughout the text, with complete answers at the end.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Vector Geometry è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Vector Geometry di Gilbert de B. Robinson in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Mathematics e Analytic Geometry. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MathematicsCategoria
Analytic Geometry1
LINES AND PLANES
1.1 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The study of geometry is essentially the study of relations which are suggested by the world in which we live. Of course our environment suggests many relations, physical, chemical and psychological, but those which concern us here have to do with relative positions in space and with distances. We shall begin with Euclidean geometry, which is based on Pythagoras’ theorem:
The square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
The statement of this fundamental result implies a knowledge of length and area as well as the notion of a right angle. If we know what we mean by length and may assume its invariance under what we call “motion,” we can construct a right angle using a ruler and compass. We define the area of a rectangle as the product of its length and breadth. To be rigorous in these things is not desirable at this stage, but later on we shall consider a proper set of axioms for geometry.
While the Greeks did not explicitly introduce coordinates, it is hard to believe that they did not envisage their usefulness. The utilization of coordinates was the great contribution of Descartes in 1637, and to us now it is a most natural procedure. Take an arbitrary point O in space, the corner of the room, for instance, and three mutually perpendicular coordinate axes. These lines could be the three lines of intersection of the “walls” and the “floor” at O; the planes so defined we call the coordinate planes. In order to describe the position of a point X, we measure its perpendicular distances from each of these three planes, denoting the distances x1, x2, x3 as in Figure 1.1 It is important to distinguish direction in making these measurements. Any point within the “room” has all its coordinates (x1, x2, x3) positive; measurements on the opposite side of any coordinate plane would be negative. Thus the following eight combinations of sign describe the eight octants of space about O:
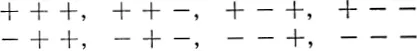
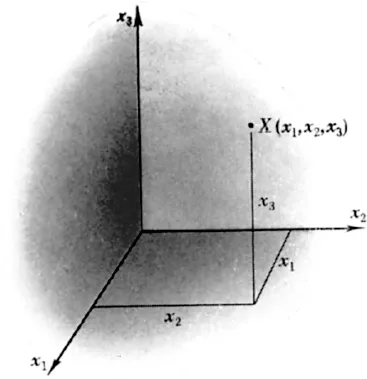
FIG. 1.1
We may describe the points on the “floor” by saying that x3 = 0; this is the equation of this ...