
eBook - ePub
Vector Geometry
Gilbert de B. Robinson
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 192 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Vector Geometry
Gilbert de B. Robinson
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
This brief undergraduate-level text by a prominent Cambridge-educated mathematician explores the relationship between algebra and geometry. An elementary course in plane geometry is the sole requirement for Gilbert de B. Robinson's text, which is the result of several years of teaching and learning the most effective methods from discussions with students.
Topics include lines and planes, determinants and linear equations, matrices, groups and linear transformations, and vectors and vector spaces. Additional subjects range from conics and quadrics to homogeneous coordinates and projective geometry, geometry on the sphere, and reduction of real matrices to diagonal form. Exercises appear throughout the text, with complete answers at the end.
Topics include lines and planes, determinants and linear equations, matrices, groups and linear transformations, and vectors and vector spaces. Additional subjects range from conics and quadrics to homogeneous coordinates and projective geometry, geometry on the sphere, and reduction of real matrices to diagonal form. Exercises appear throughout the text, with complete answers at the end.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Vector Geometry als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Vector Geometry von Gilbert de B. Robinson im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Mathematics & Analytic Geometry. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Thema
MathematicsThema
Analytic Geometry1
LINES AND PLANES
1.1 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The study of geometry is essentially the study of relations which are suggested by the world in which we live. Of course our environment suggests many relations, physical, chemical and psychological, but those which concern us here have to do with relative positions in space and with distances. We shall begin with Euclidean geometry, which is based on Pythagoras’ theorem:
The square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
The statement of this fundamental result implies a knowledge of length and area as well as the notion of a right angle. If we know what we mean by length and may assume its invariance under what we call “motion,” we can construct a right angle using a ruler and compass. We define the area of a rectangle as the product of its length and breadth. To be rigorous in these things is not desirable at this stage, but later on we shall consider a proper set of axioms for geometry.
While the Greeks did not explicitly introduce coordinates, it is hard to believe that they did not envisage their usefulness. The utilization of coordinates was the great contribution of Descartes in 1637, and to us now it is a most natural procedure. Take an arbitrary point O in space, the corner of the room, for instance, and three mutually perpendicular coordinate axes. These lines could be the three lines of intersection of the “walls” and the “floor” at O; the planes so defined we call the coordinate planes. In order to describe the position of a point X, we measure its perpendicular distances from each of these three planes, denoting the distances x1, x2, x3 as in Figure 1.1 It is important to distinguish direction in making these measurements. Any point within the “room” has all its coordinates (x1, x2, x3) positive; measurements on the opposite side of any coordinate plane would be negative. Thus the following eight combinations of sign describe the eight octants of space about O:
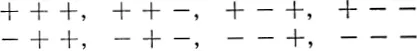
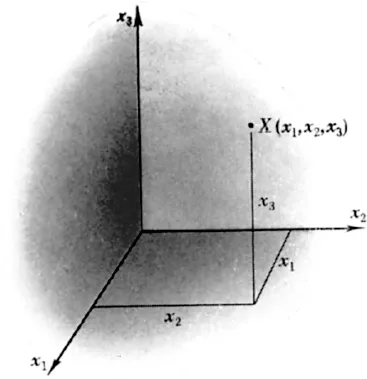
FIG. 1.1
We may describe the points on the “floor” by saying that x3 = 0; this is the equation of this ...