
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to the Theory of Groups
Paul Alexandroff, Hazel Perfect, G.M. Petersen
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 128 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to the Theory of Groups
Paul Alexandroff, Hazel Perfect, G.M. Petersen
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
This introductory exposition of group theory by an eminent Russian mathematician is particularly suited to undergraduates, developing material of fundamental importance in a clear and rigorous fashion. The treatment is also useful as a review for more advanced students with some background in group theory.
Beginning with introductory examples of the group concept, the text advances to considerations of groups of permutations, isomorphism, cyclic subgroups, simple groups of movements, invariant subgroups, and partitioning of groups. An appendix provides elementary concepts from set theory. A wealth of simple examples, primarily geometrical, illustrate the primary concepts. Exercises at the end of each chapter provide additional reinforcement.
Beginning with introductory examples of the group concept, the text advances to considerations of groups of permutations, isomorphism, cyclic subgroups, simple groups of movements, invariant subgroups, and partitioning of groups. An appendix provides elementary concepts from set theory. A wealth of simple examples, primarily geometrical, illustrate the primary concepts. Exercises at the end of each chapter provide additional reinforcement.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es An Introduction to the Theory of Groups un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a An Introduction to the Theory of Groups de Paul Alexandroff, Hazel Perfect, G.M. Petersen en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Matematica y Teoria degli insiemi. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
Categoría
MatematicaCategoría
Teoria degli insiemiChapter I
THE GROUP CONCEPT
§ 1. Introductory examples
1. Operations with whole numbers
The addition of whole numbers * satisfies the following conditions, which we call axioms of addition and which are of very great importance for all that follows:
I. Two numbers can be added together (i.e. to any two arbitrary numbers a and b there corresponds a uniquely determined number, which we call their sum: a + b).
II. The Associative Law:
For any three arbitrary numbers a, b, c we have the following identity
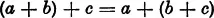
III. Among the numbers there is a uniquely determined number 0, the zero, which is such that for every number a the relation
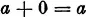
is satisfied.
IV. To every number a there corresponds a so-called inverse (or negative) number —a, which has the property that the sum a + (—a) is equal to zero:
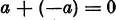
Finally yet another important condition is satisfied.
V. The Commutative Law:
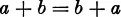
2. The rotations of an equilateral triangle
We show that it is possible to add not only numbers but also many other kinds of things, and that the above conditions remain satisfied.
First Example.—We consider all possible rotations of an equilateral triangle ABC about its centroid 0 (fig. 1). We agree to call two rotations identical if they only differ from one another by a whole number of complete revolutions (and therefore by an integral multiple of 360°*). We see without difficulty that of all possible rotations of the triangle only three rotations send it into coincidence with itself, namely, the rotations through 120°, 240°, and the so-called zero rotation, which leaves all the vertices unchanged and hence also all the sides of the triangle. The first rotation sends the vertex A into the vertex B, the vertex B into the vertex C, the vertex C into the vertex A (we say that it permutes cyclically the vertices A, B, C). The second rotation sends A into C, B into A, C into B, and therefore permutes A,C,B cyclically.
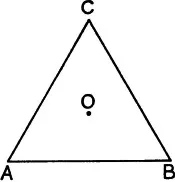
Fig. 1
Now we introduce the following natural definition: The addition of two rotations means their successive application, the first rotation followed by the second. If we add the rotation through 120° to itself, then the result is the rotation through 240°; if we add to it the rotation through 240°, then the result is the rotation through 360°, the zero rotation. Two rotations through 240° result in the rotation through 480° = 360° + 120°; their sum is therefore the rotation through 120°. If we denote the zero rotation by a0, the rotation through 120° by a1, the rotation through 240° by a2, then we obtain the following relations:
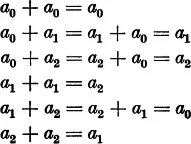
Thus the sum of any two of the rotations a0, a1, a2 is defined and is again one of the rotations a0, a1, a2 We easily convince ourselves that this addition satisfies the associative law and evidently also the commutative law. Further, there exists among these rotations a0, a1, a2 a zero rotation a0 which satisfies the...