
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to the Theory of Groups
Paul Alexandroff, Hazel Perfect, G.M. Petersen
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 128 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
An Introduction to the Theory of Groups
Paul Alexandroff, Hazel Perfect, G.M. Petersen
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This introductory exposition of group theory by an eminent Russian mathematician is particularly suited to undergraduates, developing material of fundamental importance in a clear and rigorous fashion. The treatment is also useful as a review for more advanced students with some background in group theory.
Beginning with introductory examples of the group concept, the text advances to considerations of groups of permutations, isomorphism, cyclic subgroups, simple groups of movements, invariant subgroups, and partitioning of groups. An appendix provides elementary concepts from set theory. A wealth of simple examples, primarily geometrical, illustrate the primary concepts. Exercises at the end of each chapter provide additional reinforcement.
Beginning with introductory examples of the group concept, the text advances to considerations of groups of permutations, isomorphism, cyclic subgroups, simple groups of movements, invariant subgroups, and partitioning of groups. An appendix provides elementary concepts from set theory. A wealth of simple examples, primarily geometrical, illustrate the primary concepts. Exercises at the end of each chapter provide additional reinforcement.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
An Introduction to the Theory of Groups è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a An Introduction to the Theory of Groups di Paul Alexandroff, Hazel Perfect, G.M. Petersen in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Matematica e Teoria degli insiemi. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MatematicaCategoria
Teoria degli insiemiChapter I
THE GROUP CONCEPT
§ 1. Introductory examples
1. Operations with whole numbers
The addition of whole numbers * satisfies the following conditions, which we call axioms of addition and which are of very great importance for all that follows:
I. Two numbers can be added together (i.e. to any two arbitrary numbers a and b there corresponds a uniquely determined number, which we call their sum: a + b).
II. The Associative Law:
For any three arbitrary numbers a, b, c we have the following identity
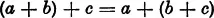
III. Among the numbers there is a uniquely determined number 0, the zero, which is such that for every number a the relation
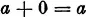
is satisfied.
IV. To every number a there corresponds a so-called inverse (or negative) number —a, which has the property that the sum a + (—a) is equal to zero:
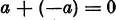
Finally yet another important condition is satisfied.
V. The Commutative Law:
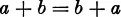
2. The rotations of an equilateral triangle
We show that it is possible to add not only numbers but also many other kinds of things, and that the above conditions remain satisfied.
First Example.—We consider all possible rotations of an equilateral triangle ABC about its centroid 0 (fig. 1). We agree to call two rotations identical if they only differ from one another by a whole number of complete revolutions (and therefore by an integral multiple of 360°*). We see without difficulty that of all possible rotations of the triangle only three rotations send it into coincidence with itself, namely, the rotations through 120°, 240°, and the so-called zero rotation, which leaves all the vertices unchanged and hence also all the sides of the triangle. The first rotation sends the vertex A into the vertex B, the vertex B into the vertex C, the vertex C into the vertex A (we say that it permutes cyclically the vertices A, B, C). The second rotation sends A into C, B into A, C into B, and therefore permutes A,C,B cyclically.
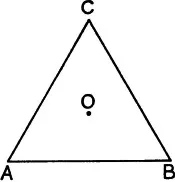
Fig. 1
Now we introduce the following natural definition: The addition of two rotations means their successive application, the first rotation followed by the second. If we add the rotation through 120° to itself, then the result is the rotation through 240°; if we add to it the rotation through 240°, then the result is the rotation through 360°, the zero rotation. Two rotations through 240° result in the rotation through 480° = 360° + 120°; their sum is therefore the rotation through 120°. If we denote the zero rotation by a0, the rotation through 120° by a1, the rotation through 240° by a2, then we obtain the following relations:
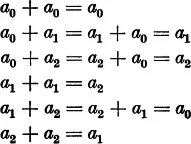
Thus the sum of any two of the rotations a0, a1, a2 is defined and is again one of the rotations a0, a1, a2 We easily convince ourselves that this addition satisfies the associative law and evidently also the commutative law. Further, there exists among these rotations a0, a1, a2 a zero rotation a0 which satisfies the...