
Statistics for Business
Derek L. Waller
- 646 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Statistics for Business
Derek L. Waller
Información del libro
Statistics for Business explains the fundamentals of statistical analysis in a lucid, pragmatic way. A thorough knowledge of statistics is essential for decision making in all corners of business and management. By collecting, organizing and analyzing statistical data you can express what you know, benchmark your current situation, and estimate future outcomes.
Based entirely on Microsoft Excel, this book covers a spectrum of statistic fundamentals from basic principles, to probability, sampling, hypothesis testing, forecasting, statistical process control and six-sigma management. This second edition is packed with features to aid understanding and help ensure that every aspect of your knowledge of statistics is applicable to practice, including:
-
- Icebreakers introducing each chapter that relate statistics to the real world, drawn from management and hospitality situations
-
- Detailed worked examples in each chapter
-
- Over 140 case-exercises complete with objective, situation, requirements, and answers
-
- A complete glossary of key terminology and formulas, mathematical relationships, and Excel relationships and functions
-
- A brand new companion website containing slides, worked-out-solutions to the case-exercises, and a test bank [coming soon]
With a clear and accessible style this book makes statistics easier to understand. It is ideal for business, management, tourism and hospitality students who want to learn how to apply statistics to the real world.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
1
Characterizing and defining statistical data
ICEBREAKER: International cost of living

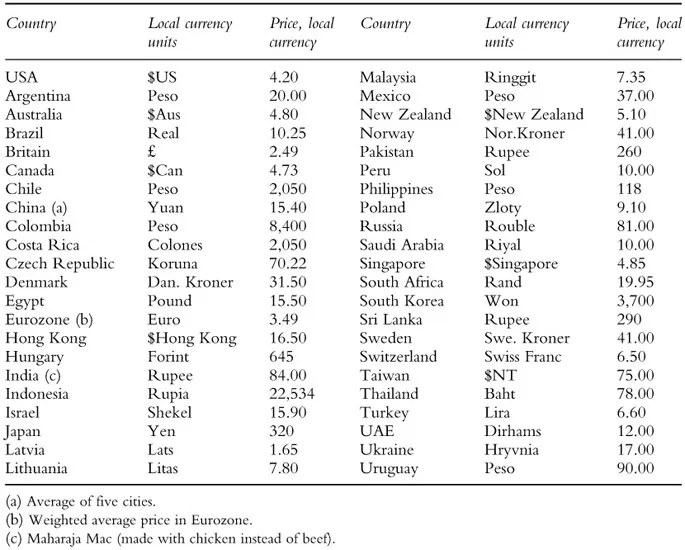
- ✓ Types of data • Quantitative data • Qualitative data • Mix qualitative/quantitative data
- ✓ Central tendency • Arithmetic mean • Median • Mode • Midrange • Weighted averages • Questionnaires and weighted averages • Geometric mean • Politics and central tendency
- ✓ Dispersion • Data spread • Range • Variance • Standard deviation • Calculation of variance and standard deviation • Deviation about the mean Coefficient of variation • Quartiles • Percentiles