
- 646 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Statistics for Business
About this book
Statistics for Business explains the fundamentals of statistical analysis in a lucid, pragmatic way. A thorough knowledge of statistics is essential for decision making in all corners of business and management. By collecting, organizing and analyzing statistical data you can express what you know, benchmark your current situation, and estimate future outcomes.
Based entirely on Microsoft Excel, this book covers a spectrum of statistic fundamentals from basic principles, to probability, sampling, hypothesis testing, forecasting, statistical process control and six-sigma management. This second edition is packed with features to aid understanding and help ensure that every aspect of your knowledge of statistics is applicable to practice, including:
- Icebreakers introducing each chapter that relate statistics to the real world, drawn from management and hospitality situations
- Detailed worked examples in each chapter
- Over 140 case-exercises complete with objective, situation, requirements, and answers
- A complete glossary of key terminology and formulas, mathematical relationships, and Excel relationships and functions
- A brand new companion website containing slides, worked-out-solutions to the case-exercises, and a test bank [coming soon]
With a clear and accessible style this book makes statistics easier to understand. It is ideal for business, management, tourism and hospitality students who want to learn how to apply statistics to the real world.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Characterizing and defining statistical data
ICEBREAKER: International cost of living

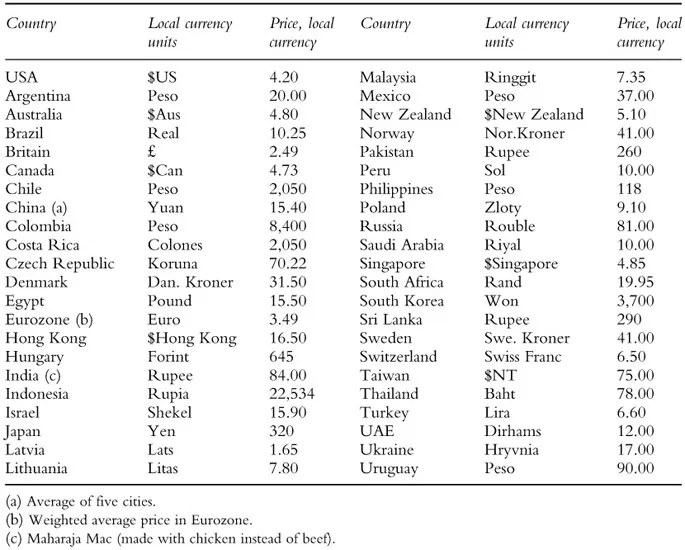
- ✓ Types of data • Quantitative data • Qualitative data • Mix qualitative/quantitative data
- ✓ Central tendency • Arithmetic mean • Median • Mode • Midrange • Weighted averages • Questionnaires and weighted averages • Geometric mean • Politics and central tendency
- ✓ Dispersion • Data spread • Range • Variance • Standard deviation • Calculation of variance and standard deviation • Deviation about the mean Coefficient of variation • Quartiles • Percentiles
Types of data
Quantitative data
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Contents
- Case-exercises
- List of figures
- About this book
- 1 Characterizing and defining statistical data (significance and essentials of numbers)
- 2 Presenting and organizing data (ways to illustrate and convince)
- 3 Essentials of probability and counting rules (foundation of uncertainty and odds)
- 4 Discrete data and probability (chance and risk applied to integer values)
- 5 Continuous distributions and probability (chance and risk in uninterrupted information)
- 6 Methods and theory of statistical sampling (appropriate testing can improve reliability)
- 7 Estimating population characteristics (giving confidence to your evaluations)
- 8 Hypothesis testing from a single population (giving assurance to assumptions that are made)
- 9 Hypothesis testing for different populations (validating further your assumptions)
- 10 Forecasting from correlated data (making objective predictions to plan operations)
- 11 Business decisions and risk (trying to avoid a disaster)
- 12 Statistical process control (SPC) (ensuring operations are according to specifications)
- 13 Six-sigma management (closing the loop to be world class)
- Case-exercises
- Appendices
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app