
eBook - ePub
Fibroids and Reproduction
Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Yakoub Khalaf, Mostafa A. Borahay, Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Yakoub Khalaf, Mostafa A. Borahay
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 130 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Fibroids and Reproduction
Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Yakoub Khalaf, Mostafa A. Borahay, Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Yakoub Khalaf, Mostafa A. Borahay
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
The most common abnormal growth of the female reproductive system, fibroids, are thought to affect the majority of women at some point during their reproductive years. This text from leading fibroid experts looks at the latest evidence on how the problem impinges on reproduction and the most up-to-date management and treatment options available to help patients with fibroids hoping to conceive.
Print versions of this book also include access to the eBook version with links to procedural videos.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Fibroids and Reproduction un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Fibroids and Reproduction de Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Yakoub Khalaf, Mostafa A. Borahay, Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Yakoub Khalaf, Mostafa A. Borahay en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Medicina y Teoría, práctica y referencia médicas. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
1
Fibroids and Reproduction: A Bird’s-Eye View
Botros R.M.B. Rizk, Candice P. Holliday, and Yakoub Khalaf
Contents
Introduction
Classification
Diagnosis
Fertility
Conception
Miscarriage
In Vitro Fertilization Outcome
References
Introduction
A fibroid (or leiomyoma) is a benign, monoclonal, smooth muscle tumor of the uterus, which usually presents as multiple lesions (Figure 1.1) but can occur as a single lesion (Figure 1.2). Fibroids are diagnosed in 20%–40% of women, generally after age 30 years, with a stable increase in incidence with increasing age [1]. This age-related increase in incidence of fibroids should be considered when looking into the relationship between fibroids and reproductive dysfunction (subfertility or miscarriage), as both are intimately age related.
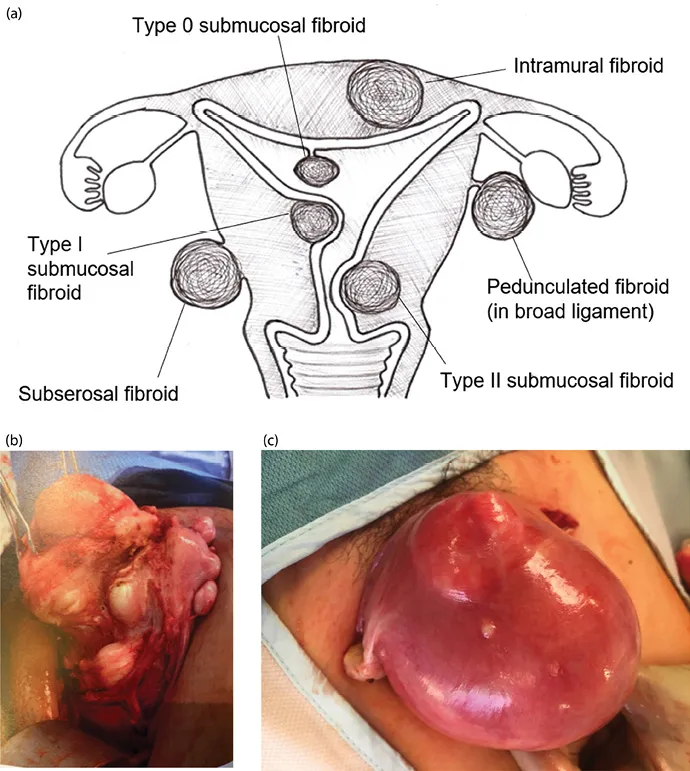
Figure 1.1 (a) Varying fibroid locations within the uterus; (b) multiple fibroids—intramural, subserosal, and submucosal; (c) uterus enlarged with intramural fibroids.
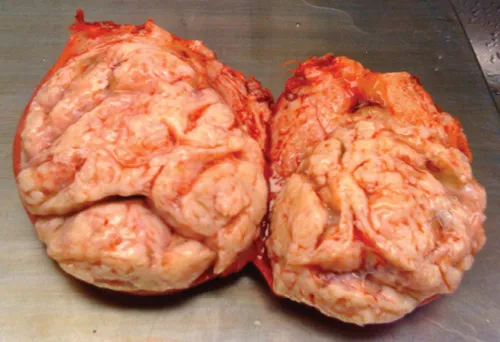
Figure 1.2 Solitary large fibroid.
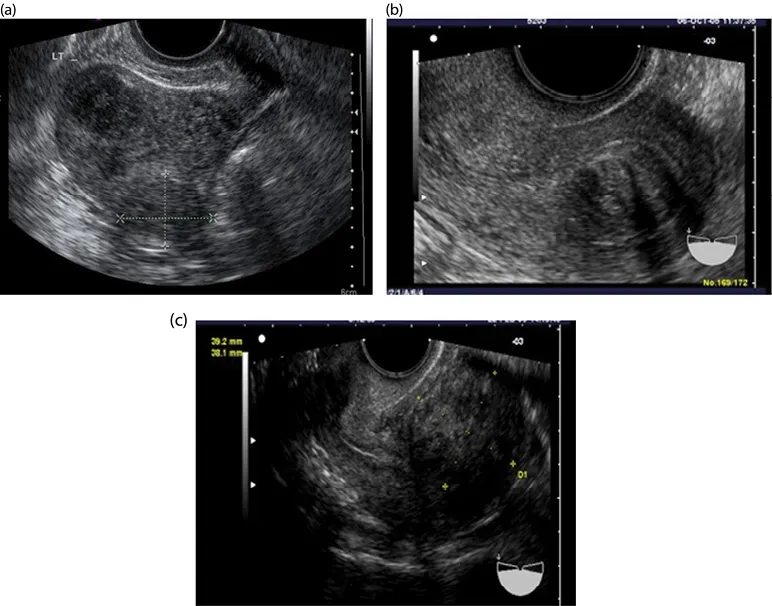
Figure 1.3 (a–c) Intramural fibroids.
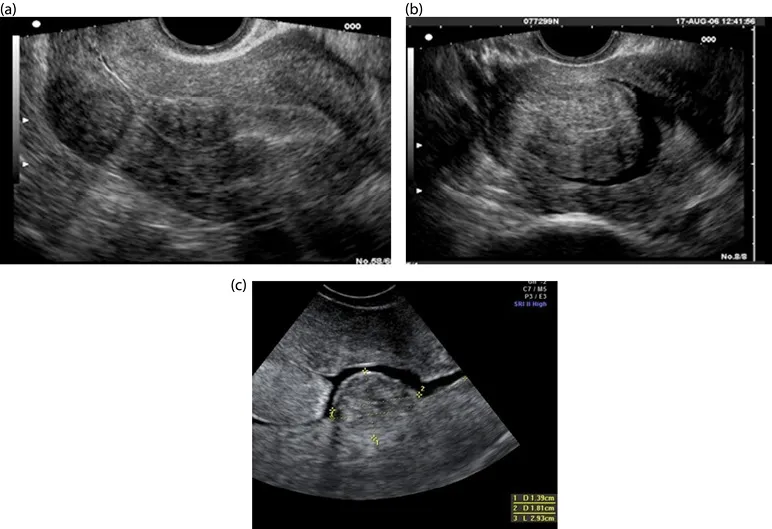
Figure 1.4 (a–c) Submucosal fibroids.
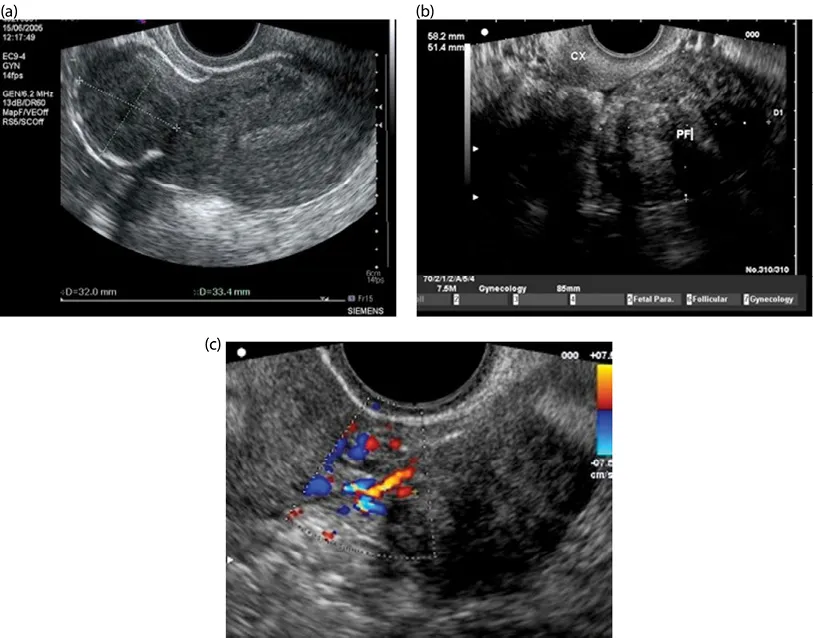
Figure 1.5 (a) Subserosal fibroid; (b) pedunculated fibroid; (c) Doppler scan showing feeder vessels of pedunculated fibroid.
Although it is biologically plausible and clinically evident that fibroids are associated with reproductive dysfunction (see Chapter 2), a cause-effect relationship has not been established.
Most symptomatic fibroids can be diagnosed clinically, but crucial clinical information can be obtained by one imaging modality or another.
Ultrasound is a noninvasive imaging modality that is well tolerated by patients, and it is a rather inexpensive way to obtain a relatively accurate assessment of fibroids within the pelvis (see Chapter 8). Assessing fibroid size and location can be beneficial for planning surgery or for monitoring changes in fibroids over time (Figures 1.3–1.5).
In some complex cases (multiple fibroids, previous surgery, and associated morbidities), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide additional valuable information that could help in planning surgery or guide the choice of alternative therapeutic approaches, such as the use of uterine artery embolization (UAE) or MRI-guided focused ultrasound (see Chapter 7).
Classification
When fibroids develop from the uterine wall but distort the uterine cavity, it is helpful to detail the degree of uterine cavity impingement (see Chapter 7) with the Wamsteker and de Blok classification [2]. Following are the types of fibroids:
•0: 100% of the fibroid is pedunculated into the uterine cavity
•I: Greater than 50% of the fibroid is within the uterine cavity
•II: Less than 50% of the fibroid is within the uterine cavity (i.e., greater than 50% of the fibroid is within the myometrium)
It can be difficult to assess on two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound scan what type of fibroid a patient has. Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound and saline infusion sonohysterography are often used to obtain that information (Figures 1.6–1.8). A diagnosis that is accurate is critical to determine presurgical treatment, what type of surgery would be best, and what sort of prognosis a patient can expect [2]. A comparable classification system has been suggested for intramural and subserosal fibroids in order to describe what degree of myometrial involvement exists (see Chapter 2 for the detailed classification system). Three-dimensional ultrasound is becoming an increasingly valuable imaging tool to map out the relationship between the fibroid and the endometrial cavity.
Diagnosis
Two-dimensional ultrasound is the traditional manner of imaging fibroids, although other imaging modalities exist. For ideal visualization of fibroids, especially of their outline, the best technique uses a transvaginal scan (TVS) (see Figures 1.3–1.5). With a transvaginal approach, the ultrasound probe is closer to the uterus, which allows a higher frequency to be used. This higher frequency provides better definition of the tissues. A patient should empty her bladder first before a TVS is done. The TVS transducer is curvilinear, multifrequency, and endocavity, with a central frequency that is usually 6.5 MHz. The ultrasound beam can be highly attenuated by fibroids due to fibroids’ dense and mixed tissue composition. Thus, poor throug...