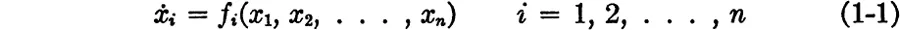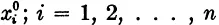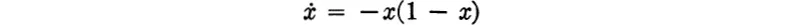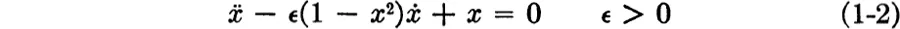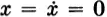![]()
Part I
Introduction and Background Material
![]()
1: Introduction
Most physical systems are nonlinear. We shall assume the evolution of the physical system is governed by a real ordinary differential equation; that is, the state x(t) = (x1(t), x2(t), . . . , xn(t)) of the physical system at time t is a point along the solution of the differential system
which passes through the point
, at time
t =
t0.
In general, the functions fi are nonlinear functions of the state variables x1, x2, . . . , xn. For the sake of simplicity in analyzing (1-1), the functions fi are frequently replaced by linear functions. In many cases this is sufficient, but there are phenomena which cannot be explained by analysis of the linear approximation.
The purpose of the present book is to concentrate on some aspects of differential equations which depend very strongly upon the fact that (1-1) is nonlinear.
The basic quality of a linear system (1-1) is (1) the sum of any two solutions of (1-1) is also a solution (the principle of superposition) and (2) any constant multiple of a solution of (1-1) is also a solution. Consequently, knowing the behavior of the solutions of (1-1) in a small neighborhood of the origin, x1 = x2 = · · · = xn = 0, implies one knows the behavior of the solutions everywhere in the state space; that is, globally. Furthermore, if one has a periodic solution of a linear system (1-1), then it cannot be isolated since any constant multiple of a solution is also a solution.
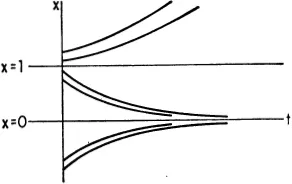
In nonlinear systems none of the above properties need be true. In fact, there is no principle of superposition, the behavior of solutions is generally only a local property, and there may be isolated periodic solutions (except for a phase shift). A simple example illustrating the local property of the behavior of solutions is
whose solutions are shown in Fig. 1-1.
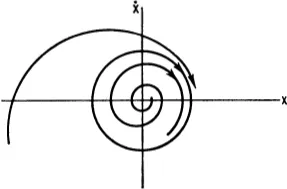
The most classical example of a system which has an isolated periodic solution (except for a shift in phase) is the van der Pol equation
whose trajectories in the
plane are shown in
Fig. 1-2. The closed curve
C has the property that all other trajectories approach it as
t → ∞ except, of course, the trajectory which passes through the equilibrium point
. This is a phenomenon which is due to the nonlinear structure of the system and could never be explained by a linear analysis. Such an oscillation is called
self-
excited.
Fig. 1-1
Fig. 1-2
Another interesting phenomenon that may occur in nonlinear systems is the following: Suppose system (1-1) is linear and apply a periodic forcing function of period T to (1-1). If the unforced system has no periodic solution, then there can never be an isolated periodic solution of any period except T. In nonlinear systems, this is not the case and isolated periodic solutions of period mT, where m i...