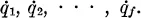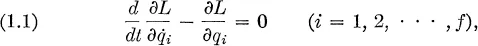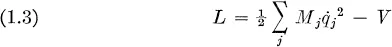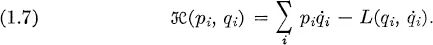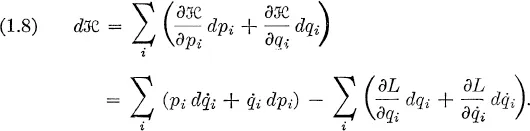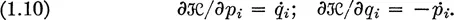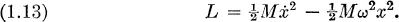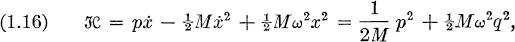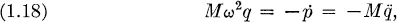Elementary Statistical Physics
Charles Kittel
- 240 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Elementary Statistical Physics
Charles Kittel
À propos de ce livre
Noteworthy for the philosophical subtlety of its foundations and the elegance of its problem-solving methods, statistical mechanics can be employed in a broad range of applications — among them, astrophysics, biology, chemistry, nuclear and solid state physics, communications engineering, metallurgy, and mathematics. Geared toward graduate students in physics, this text covers such important topics as stochastic processes and transport theory in order to provide students with a working knowledge of statistical mechanics.
To explain the fundamentals of his subject, the author uses the method of ensembles developed by J. Willard Gibbs. Topics include the properties of the Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein distributions; the interrelated subjects of fluctuations, thermal noise, and Brownian movement; and the thermodynamics of irreversible processes.
Negative temperature, magnetic energy, density matrix methods, and the Kramers-Kronig causality relations are treated briefly. Most sections include illustrative problems. Appendix. 28 figures. 1 table.
Foire aux questions
Informations
Fundamental principles of statistical mechanics
| Reference: | H. Goldstein, Classical mechanics, Addison-Wesley, Cambridge, Mass., 1953, Chap. 7. |