
eBook - ePub
Applications of Tensor Analysis
A. J. McConnell
This is a test
Partager le livre
- 352 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Applications of Tensor Analysis
A. J. McConnell
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
This standard work applies tensorial methods to subjects within the realm of advanced college mathematics. In its four main divisions, it explains the fundamental ideas and the notation of tensor theory; covers the geometrical treatment of tensor algebra; introduces the theory of the differentiation of tensors; and applies mathematics to dynamics, electricity, elasticity, and hydrodynamics.
Partial contents: algebraic preliminaries (notation, definitions, determinants, tensor analysis); algebraic geometry (rectilinear coordinates, the plane, the straight line, the quadric cone and the conic, systems of cones and conics, central quadrics, the general quadric, affine transformations); differential geometry (curvilinear coordinates, covariant differentiation, curves in a space, intrinsic geometry of a surface, fundamental formulae of a surface, curves on a surface); applied mathematics (dynamics of a particles, dynamics of rigid bodies, electricity and magnetism, mechanics of continuous media, special theory of relativity).
Partial contents: algebraic preliminaries (notation, definitions, determinants, tensor analysis); algebraic geometry (rectilinear coordinates, the plane, the straight line, the quadric cone and the conic, systems of cones and conics, central quadrics, the general quadric, affine transformations); differential geometry (curvilinear coordinates, covariant differentiation, curves in a space, intrinsic geometry of a surface, fundamental formulae of a surface, curves on a surface); applied mathematics (dynamics of a particles, dynamics of rigid bodies, electricity and magnetism, mechanics of continuous media, special theory of relativity).
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Applications of Tensor Analysis est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Applications of Tensor Analysis par A. J. McConnell en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Mathematics et Vector Analysis. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
Sujet
MathematicsSous-sujet
Vector AnalysisPART I
Algebraic Preliminaries
CHAPTER I
NOTATION AND DEFINITIONS
1. The indicial notation.
The notation of the absolute differential calculus or, as it is frequently called, the tensor calculus, is so much an integral part of the calculus that once the student has become accustomed to its peculiarities he will have gone a long way towards solving the difficulties of the theory itself. We shall therefore devote the present chapter to a discussion of the notation alone, applying it briefly to the theory of determinants, and we shall postpone to the next chapter the tensor theory proper.
If we are given a set of three independent variables, they may be denoted by three different letters, such as x, y, z, but we shall find it more convenient to denote the variables by the same letter, distinguishing them by means of indices. Thus we may write the three variables x1, x2, x3, or, as they may be more compactly written,
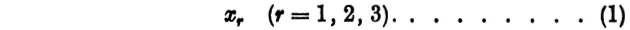
Now in (1) we have written the index r as a subscript, but we could equally well have used superscripts instead, so that the variables would be written x1, x2, x3, or
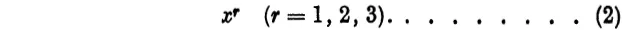
Here it must be understood that xr does not mean that x is raised to the rth power, but r is used merely to distinguish the three variables. In the sequel we shall have occasion to use both subscripts and superscripts, and in the next chapter we shall give a special significance to the position of the index. In fact we shall find that, in accordance with the convention adopted later, the form (2) is the appropriate one for our variables and not (1).
A homogeneous linear function of the variables is obviously of the form
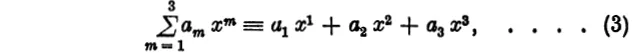
where a1, a2, a3 are constants. Thus the coefficients of a linear form can be written
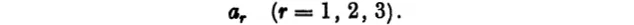
Systems of quantities, which, like xr and ar, depend on one index only, are called systems of the first order or simple systems, and the separate terms, x1, x2, x3 and a1, a2, a3 are called the elements or components of the system. It is obvious that a system of the first order has three components. More...